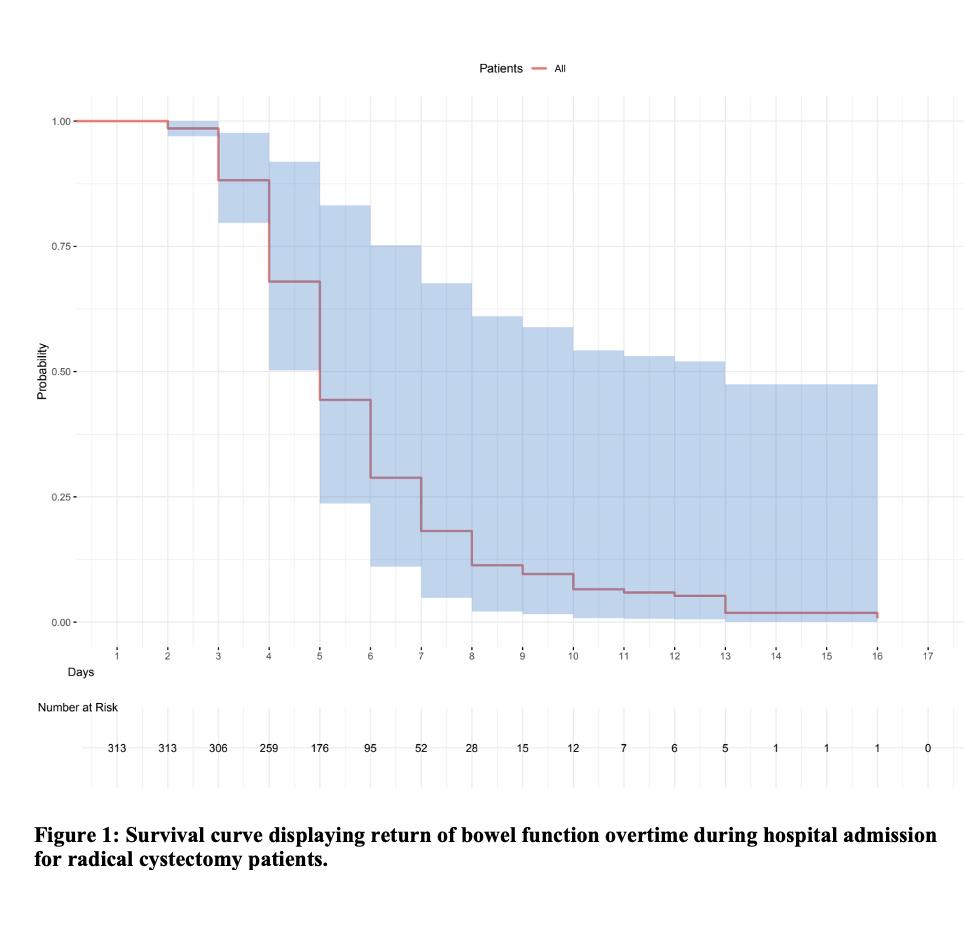
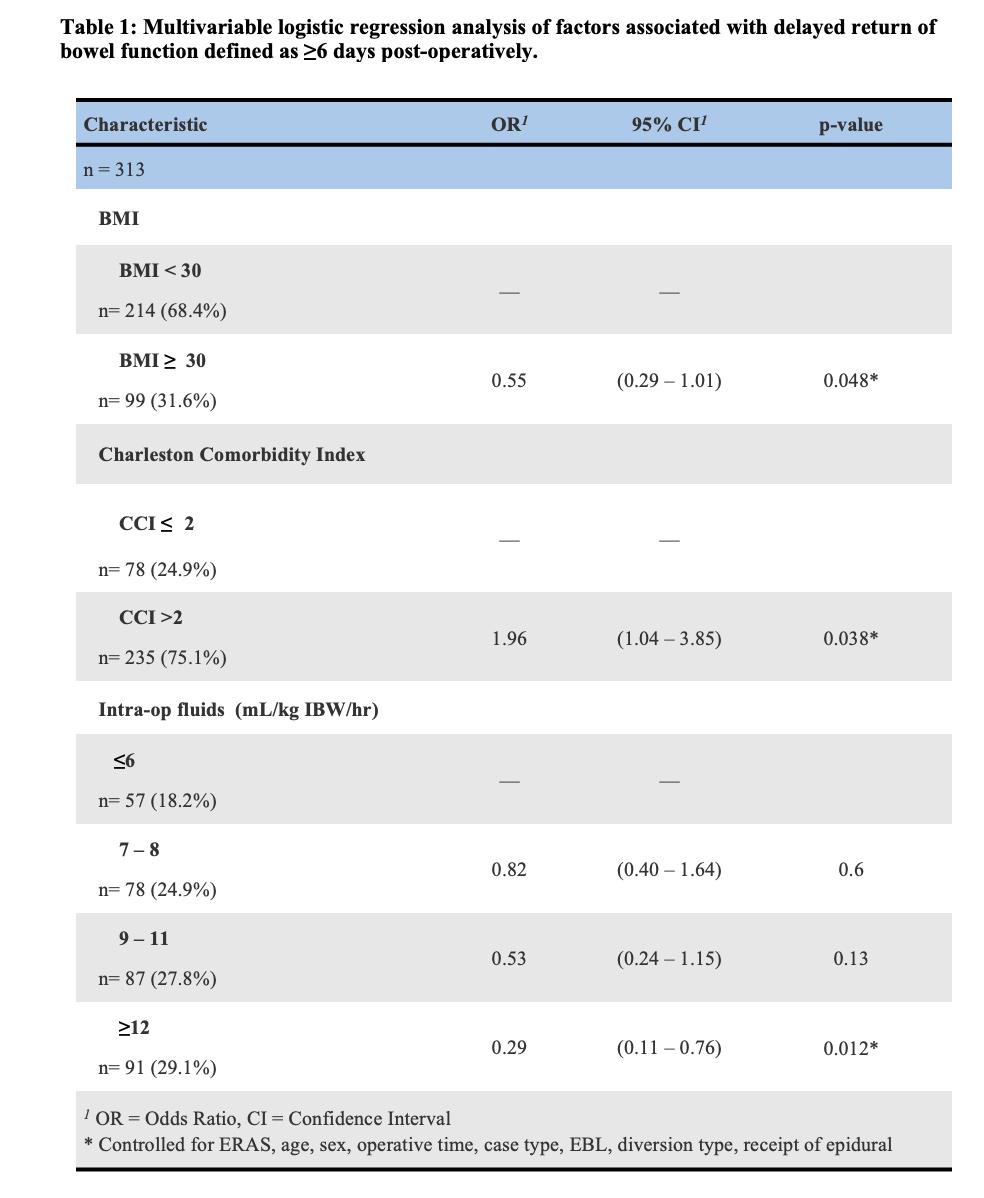
BACKGROUND:Radical Cystectomy (RC) is standard of care for Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer (MIBC). Post-operative ileus is a common complication following surgery that can lead to prolonged hospital stay. Numerous protocols to improve return of bowel function (ROBF) been described. In this study, we sought to evaluate modifiable factors associated with delayed return of bowel function (ROBF) in a real-world contemporary cohort in an effort to improve patient-related outcomes. METHODS:A prospectively maintained RC database of 313 patients (pts) with complete 90d follow-up from 2015-2023 were retrospectively reviewed. Delayed ROBF was defined as ≥6 days without a bowel movement. Factors associated with delayed ROBF were assessed by comparison to normal ROBF using multivariable logistic regression. Day of discharge was used if no bowel movement was charted during admission. Covariates included age, sex, Charleston Comorbidity Index (CCI) >2, BMI ≥30, case type (open or robotic), estimate blood type (EBL), diversion type, operative time, intraoperative fluid given by kilogram ideal body weight (IBW) per hour, ERAS, and receipt of epidural. RESULTS:230/313 (73.5%) pts had ROBF by POD6 (Figure 1). Patient factors associated with delayed ROBF were CCI>2 with an odds ratio (OR) of 1.96 (95% CI, 1.04-3.85, p=.038). BMI ≥ 30 was protective against delayed ROBF (OR of 0.55, [95% CI, 0.39-1.01], p=.048). Most peri-operative factors were not associated with ROBF including case type, participation in ERAS protocol, epidural use, and diversion type (data not shown). Receipt of greater amounts of intraoperative fluid intraoperative by IBW (≥12 mL/kg IBW/hr) was the most protective against delayed ROBF, (OR 0.29, [95% CI, 0.11-0.76], p=.012), (Table 1). CONCLUSIONS:As a complex surgery, delayed ROBF is a common complication of RC that is multifactorial. We find CCI>2 is independently associated with delayed ROBF, which could be related to decreased rates of early mobilization during admission. BMI>30 was shown to be protective against delayed ROBF, potentially highlighting the importance of perioperative nutritional status. The receipt of higher volumes of fluid intraoperatively by IBW did not lead to delayed ROBF. This would suggest goal directed fluid therapy intraoperatively plays an important role in reducing bowel edema and delayed return of bowel function. This is further supported in that ERAS protocols did not appear to be statistically significant.