BACKGROUND: While cancer screening and diagnosis declined sharply during the COVID pandemic, changes to specific prostate cancer-related services has not been directly evaluated. We aimed to estimate changes in the use of diagnostic, risk stratification and treatments for prostate cancer in the Medicare population.
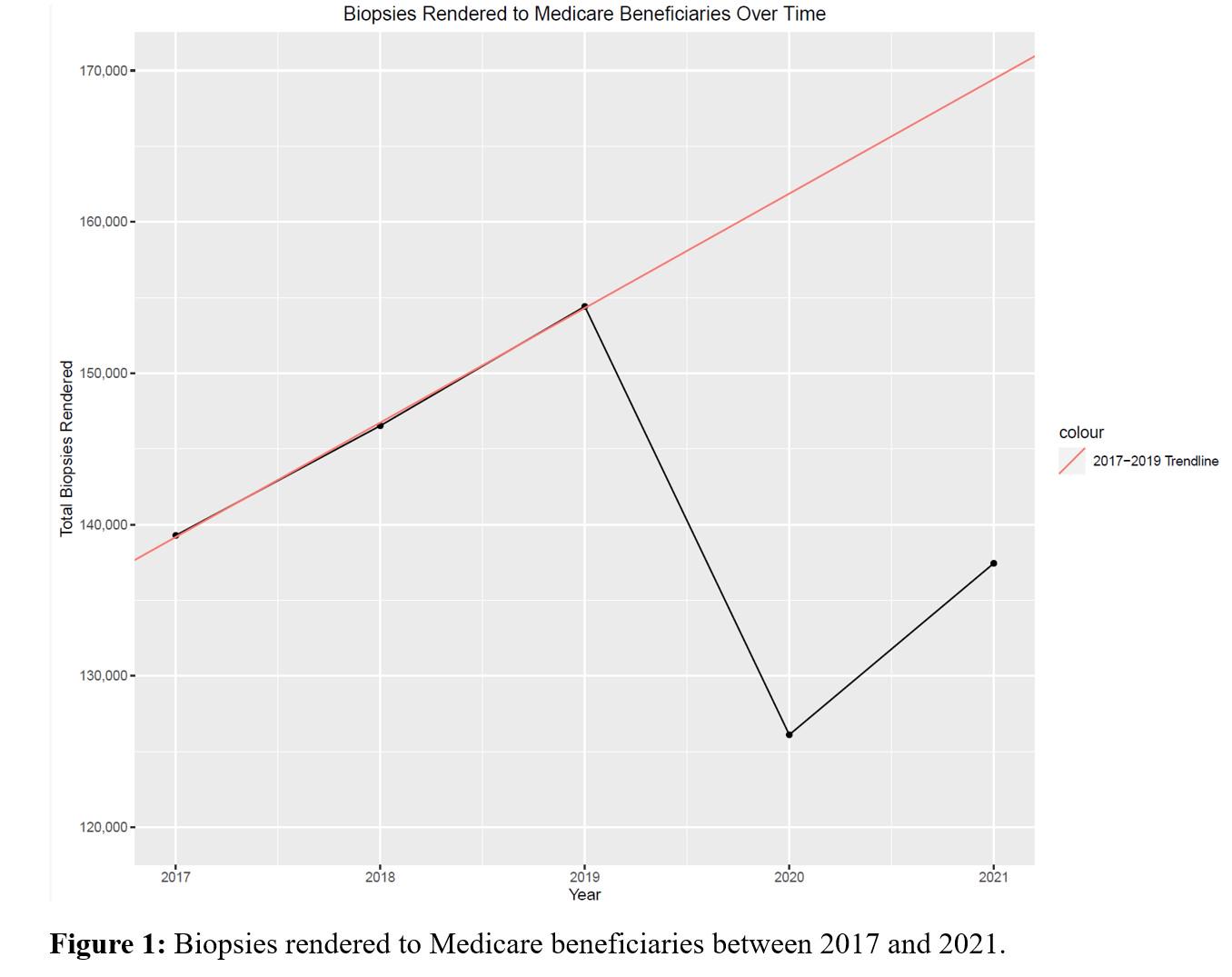
METHODS: We queried the 2017 - 2021 Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Medicare Physician & Other Practitioners databases to identify services billed for prostate biopsy, pelvic MRI, and radical prostatectomy. We analyzed individual services provided by urologists based on current procedural terminology (CPT) claim codes. The primary outcome was change in the volume of services provided per year. To estimate changes in 2020 accounting for prior usage trends, we created a line of best fit using 2017 - 2019 data to estimate the number of services rendered in 2020 if prior usage trends were to have continued. RESULTS: Between 2019 and 2020 there was a relative 18.3% reduction in prostate biopsies, a 16.2% reduction in transrectal ultrasounds (TRUS), a 3.0% reduction in pelvic MRIs, and a 12.2% reduction in radical prostatectomy among Medicare beneficiaries. Medicare spending to physicians decreased in aggregate by $6,202,708 for prostate biopsy, $1,216,376 for TRUS, and $1,755,461 for prostatectomy. The number of prostate genetic tests performed in 2020 relatively increased by 50% (7,756). Prostate biopsy and radical prostatectomy increased in 2021 relative to 2020, however remained 11% and 9.3% lower than to pre-pandemic utilization. We estimate that 35,761 fewer prostate biopsies were performed in 2020 than predicted using 2017-2019 trends (Figure 1). CONCLUSIONS:
There were significant declines in the use of prostate biopsy and radical prostatectomy during the COVID pandemic among the Medicare population with corresponding declines in Medicare spending. Further studies should examine the longer-term impact of reductions in prostate cancer diagnosis and treatment.
| CPT Code | Description |
| 55705 | Biopsy, prostate; incisional, any approach |
| 76872 | Ultrasound, transrectal |
| 72197 | Mri scan of pelvis before and after contrast |
| 0005U, 81551, 0047U, 81541, 81542 | Genomic test: Prostate mRNA gene expression profiling by real-time PCR |
| 55866, 55831, 55840, 55842, 55845, 55866 | Prostatectomy: Any approach |