Background: With advancements in multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) fusion technology, targeted biopsy (TB) has increasingly become integrated into the diagnostic workup for men with risk factors for prostate cancer (PCa) in conjunction with standard 12 core systematic biopsy (SB). The aim of this study is to evaluate the accuracy of TB in the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer (csCAP) compared to SB.
Methods: We reviewed our centerís mpMRI database to identify patients who were diagnosed with csCAP, defined as GG2 and above (GG2+), between the years of 2016 to 2021. This included both patients without a history of PCa and those on active surveillance (AS). All patients underwent mpMRI followed by combined targeted and systematic biopsies. Biopsy findings were then analyzed and stratified by grade group (GG) and PIRADS score respectively.
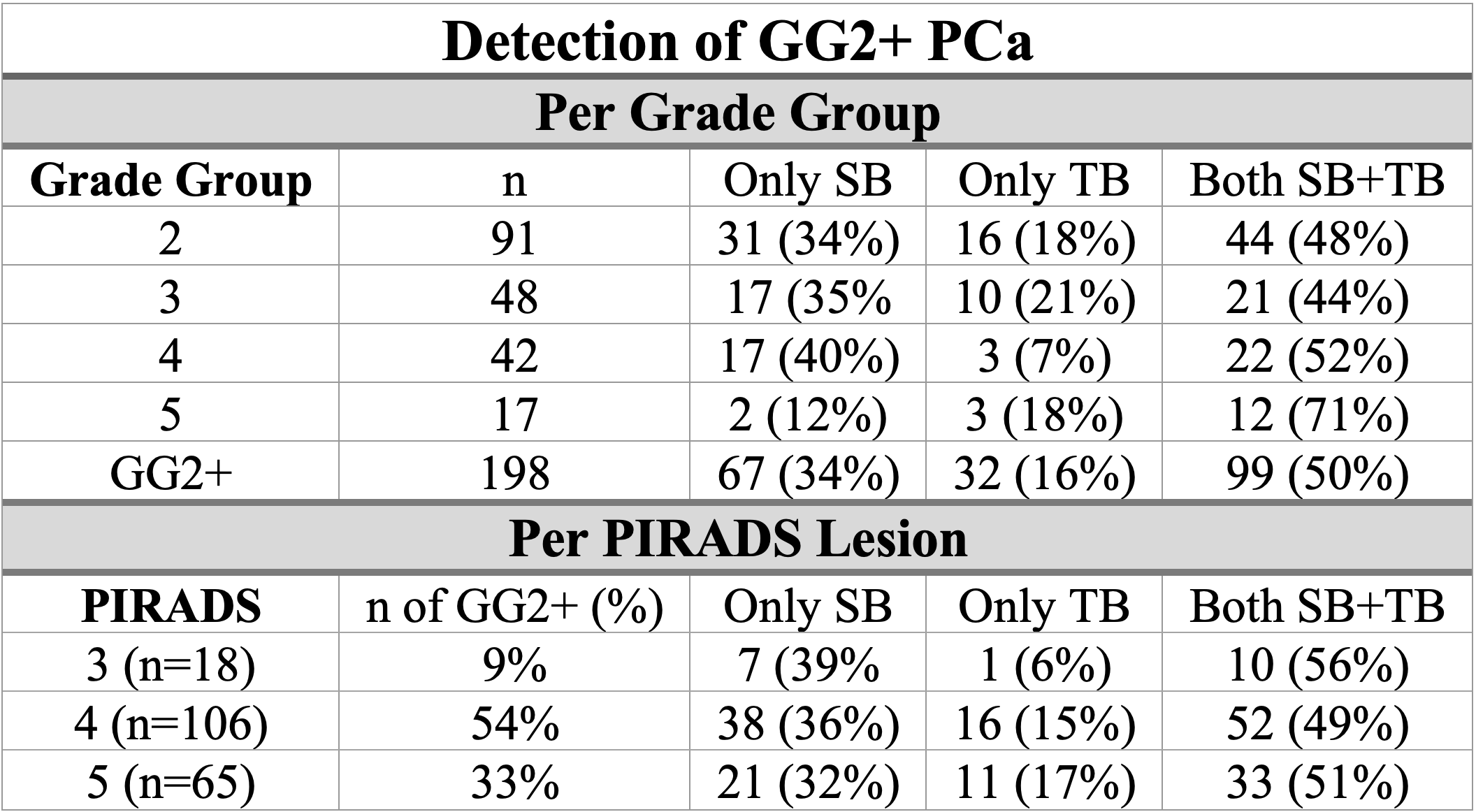
Results: 198 biopsies resulted in csPCa. Median age was 68 (IQR 63-73) and median PSA 7.0 ng/mL (5.1-9.9). 105 (53%) had no prior diagnosis of PCa, and 93 (47%) were on AS. Overall, TB alone identified 32 GG2+ cancers (16%) compared to SB alone 67 (34%). Table 1 stratifies the findings based on GG and PIRADS. Half of the GG2+ cancers 99 (50%) were detected by both modalities. The percentage detected on both approaches increased as pathology progressed from GG2 (48%) to GG5 (71%) and was stable across PIRADS (range 49%-56%). The percentage of TB missing a GG2+ cancer decreased with highest grade disease GG5 (2; 12%).
Conclusion: In this study, one third of csPCa was detected by SB alone and missed on TB. These findings add to literature suggesting that template biopsies are important for both initial and surveillance biopsies, across PIRADS lesions. To improve accuracy of targeted fusion results, further investigation into multimodal risk assessments, risk stratification, and operator use are warranted.