Extracellular miRNA as a marker of invasive urothelial cancer
Esther L. Finney, MD, Thomas Kalantzakos, BS, Travis Sullivan, MS, Kimberly Rieger-Christ, PhD.
Lahey Hospital and Medical Center, Burlington, MA, USA.
BACKGROUND: Determination of muscle invasion is critical in the staging, prognosis, and treatment of urothelial carcinoma (UC). MicroRNA (miRNA) have been shown to be dysregulated in both non- and muscle-invasive UC and are thought to serve an important role in tumor progression. Extracellular vesicle (EV) miRNA can be easily isolated from body fluids, such as urine. They are a novel target for development of diagnostic biomarkers that are non-invasive and overcome the constraints of tissue biopsies. We sought to identify differential expression of EV miRNA between noninvasive and invasive UC and investigate the effect of identified miRNA on tumor pathogenesis in UC cell lines.
METHODS: EV miRNA was isolated from the urine of patients with biopsy-proven non-invasive (n= 14) or invasive bladder UC (n=15). Urine was collected pre-operatively and specimens were grouped according to invasion at the time of transurethral resection. Twelve miRNA were assayed via PCR and those with increased expression in invasive specimens were further examined. miRNA from four UC cell lines (J82, UMUC, RT112, and CUBIII) and EV miRNA from cell-free culture media from those lines were isolated and PCR performed for in-vitro validation. Two UC cell lines, UMUC (invasive) and CUBIII (non-invasive), were then transfected with pre-miRNA of the previously identified miRNA. Cell proliferation was evaluated at 24 and 48 hrs in the transfected cell lines by MTT assays. Potential miRNA tumor suppressor protein targets were identified based on predicted interactions, and their levels were determined via Western blots.
RESULTS: Three miRNA (miR-222-3p, miR-320b, and miR-423-5p) had increased expression in the urine EVs of patients with invasive UC (p<0.05). These miRNA were also upregulated in the EVs of cultured cells with an invasive phenotype. Transfection of miR-320b and miR-222-3p was successful into both UC cell lines and increased proliferation in both the noninvasive and invasive cell lines (p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS: Urine EV miR-320b and miR-222-3p are upregulated in invasive UC and may have a role in tumor progression. They are promising biomarkers that could improve diagnostic precision as well as serve as potential therapeutic targets. 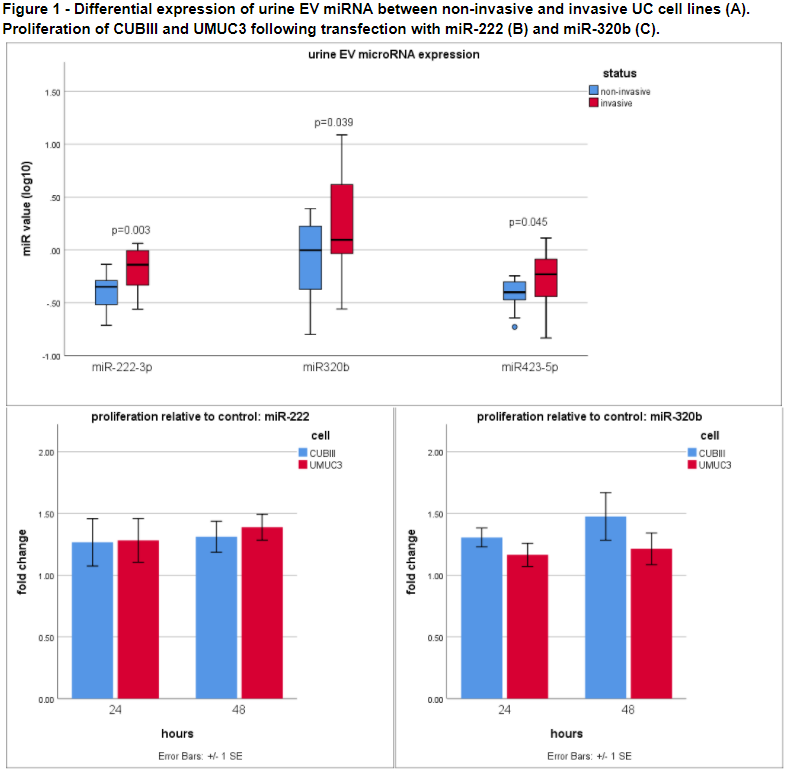
Back to 2021 Abstracts
