MicroRNA let-7f-5p Is A Novel Biomarker Of Recurrence And A Potential Therapeutic Opportunity In Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
Kevin Shee, PhD1, Margaret R. Karagas, PhD1, Carmen J. Marsit, PhD1, Alan R. Schned, MD2, Jason R. Pettus, MD2, David Armstrong, BS1, Todd W. Miller, PhD1, John D. Seigne, MD2, Angeline S. Andrew, PhD1
1Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Lebanon, NH, 2Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, NH
BACKGROUND: Among patients diagnosed with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC), 50% to 75% experience recurrences within 6 to 12 years of diagnosis, and 10% to 30% of tumors progress to muscle-invasive disease. The need to screen for these events every 3-6 months by cystoscopy makes bladder cancer one of the most expensive malignancies. Non-coding RNAs, particularly the microRNAs (miRNAs), have emerged as useful prognostic biomarkers in cancer. The objective of this study was to identify reproducible prognostic miRNAs in resected non-muscle invasive bladder tumor tissue that are predictive of the recurrent tumor phenotype as potential biomarkers and molecular therapeutic targets.
METHODS: Two independent cohorts of NMIBC patients from the New Hampshire Population Cohort and Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center were analyzed using a biomarker discovery (n=178) and validation (n=38) approach, respectively. We isolated tumor tissue RNA and assessed expression of ~800 miRNAs, and performed recurrence free survival (RFS) analyses using a multivariable model adjusted for sex, age, multiplicity, tumor size, stage, and grade. Urine and plasma samples were obtained from available patients from the validation cohort and analyzed for miRNA expression. To assess the therapeutic potential of targeting Lin28, a known negative regulator of Let-7f-5p, Lin28 primers and small molecule inhibitor Lin28 1632 were obtained and assayed using RT-PCR, cell viability, and scratch assays in NMIBC cell line HTB-2.
RESULTS: miRNA Let-7f-5p showed the strongest association with recurrence across both the NH population cohort (p=0.039) and the DHMC cohort (p=0.065). Survival analyses stratified by median Let-7f-5p expression confirmed longer RFS in the patients with high Let-7f-5p for both discovery and validation cohorts (p=0.011 and 0.065; Figure 1A/B). Let-7f-5p was found to have potential clinical utility as a biomarker, and levels in urine and plasma were both found to be significantly correlated with levels in tumor tissue (P=0.0004 and 0.014, respectively). Finally, inhibition of Lin28 with Lin28 1632 significantly increased levels of Let-7f-5p expression (p=0.0003; Figure 1C) and led to significant inhibition of viability and migration of HTB-2 cells (both p<0.0001; Figures 1D/E).
CONCLUSIONS: In this study, we have identified Let-7f-5p as a novel miRNA biomarker of recurrence in NMIBC tumors, and show that patients with high Let-7f-5p have longer RFS. We further show that targeting Lin28, a negative regulator of Let-7f-5p, represents a novel therapeutic opportunity in NMIBC. 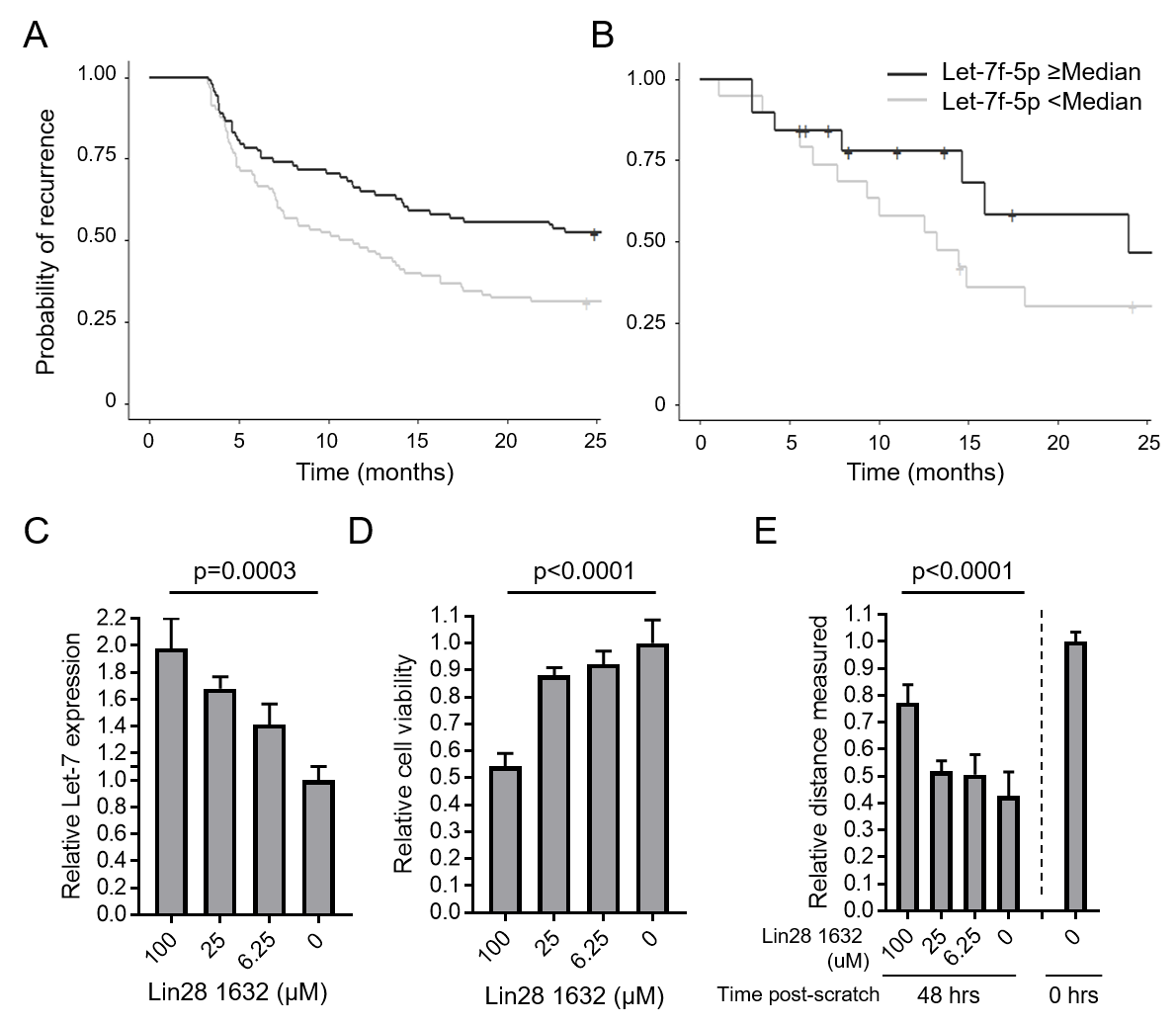
Back to 2019 Abstracts
