The Intrinsic Nervous System of the Ureter
Alberto Pieretti, MD; Emily Arciero, BS; Ryo Hotta, MD; Allan M Goldstein, MD
Massachusetts General Hospital, Brookline, MA
BACKGROUND: The Autonomic Nervous System of the ureter has been described as an extrinsic component arriving from celiac, aortorenal and mesenteric ganglia. The Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) have been reported to be present in the renal pelvis and proximal ureter, where they regulate ureteral peristalsis. We hypothesized that the ureter has as intrinsic, neural crest-derived nervous system along its entire length.
METHODS:
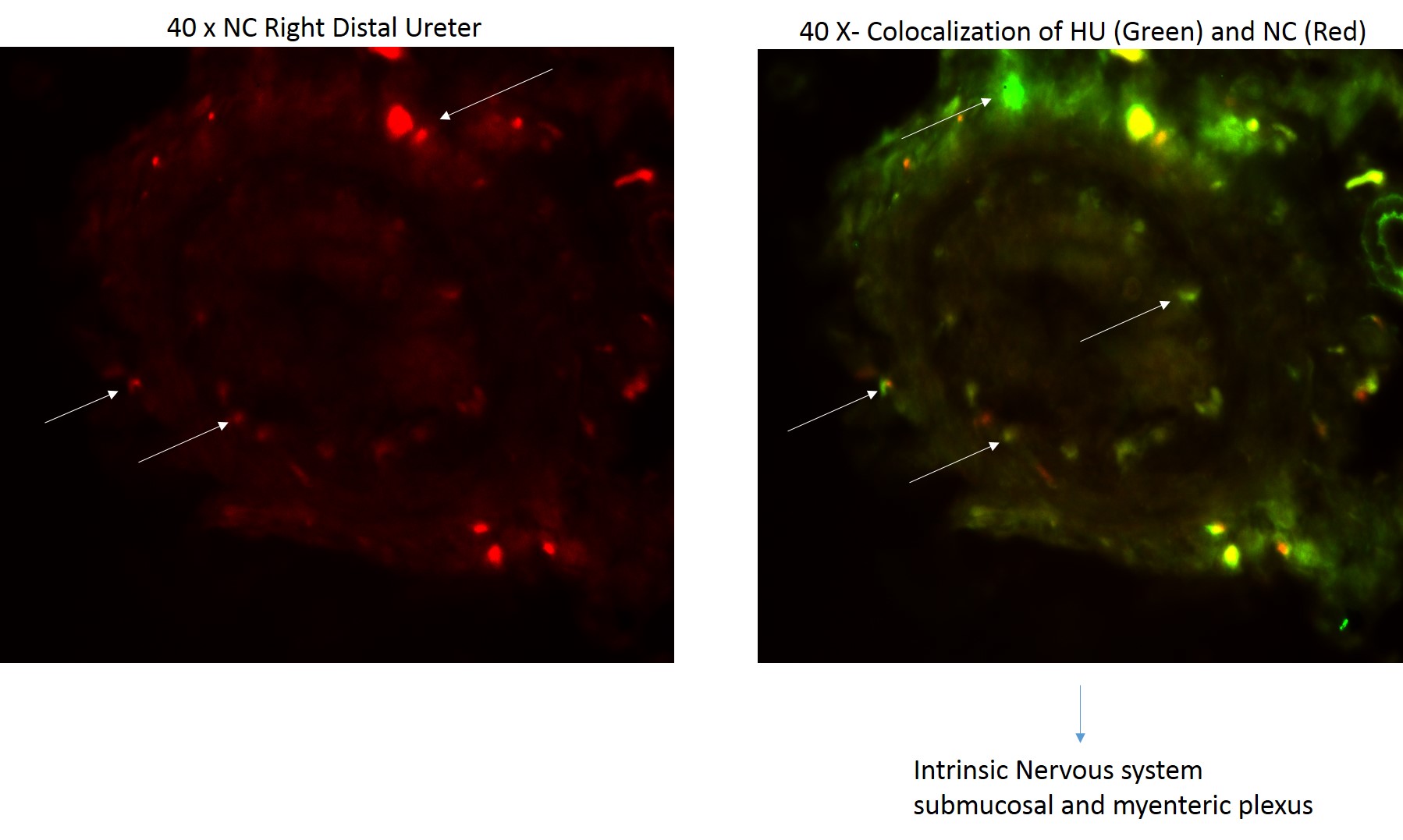
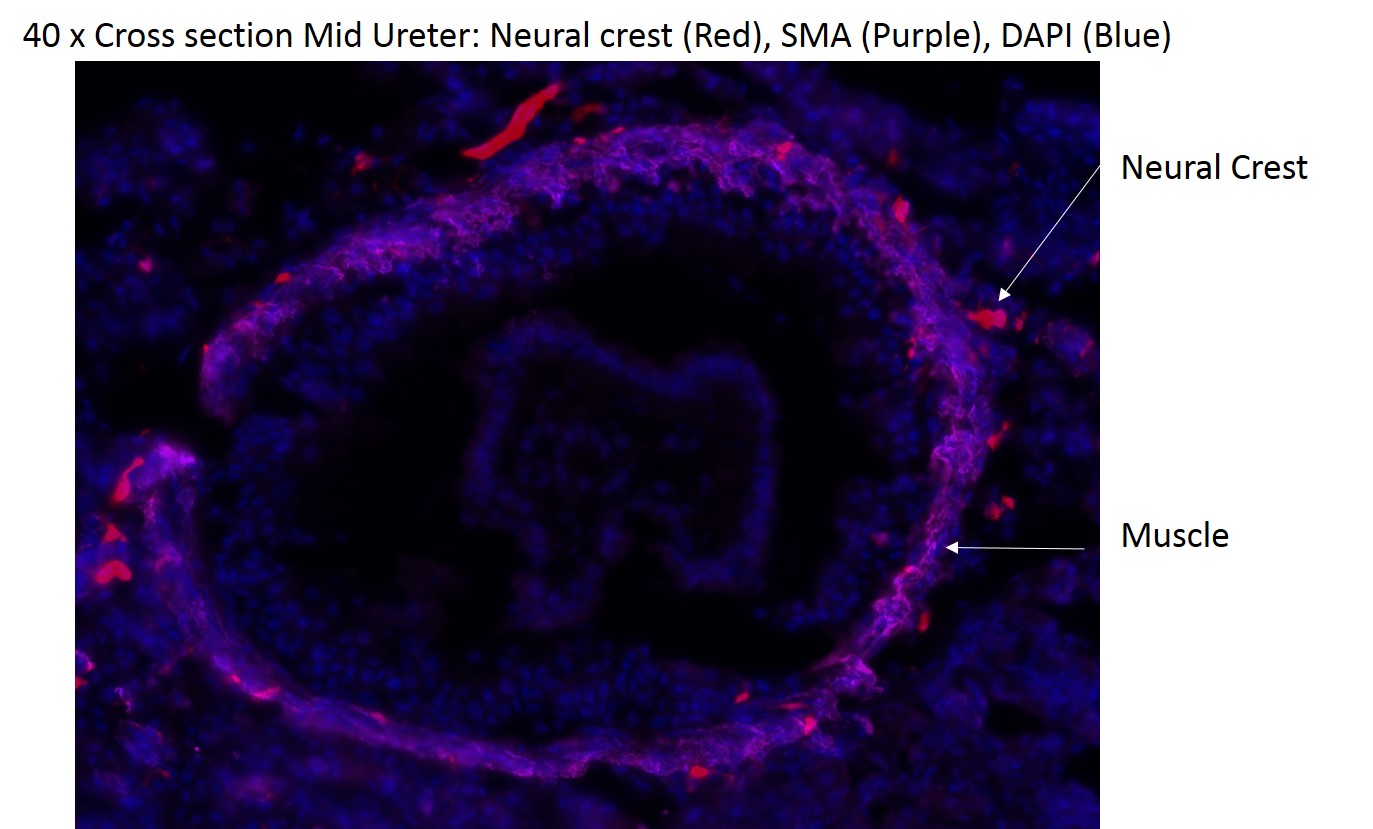
We tested our hypothesis by isolating kidney, ureters and bladder of 3 week-old transgenic mice in which the expression of Rosa 26 tdtomato red fluorescent protein is expressed in the neural crest cell (NCC) lineage (Wnt-Cre, Rosa Tdtomato). Whole mount images were taken. The ureter was divided into 3 segments (proximal, mid, distal). Immunofluorescence with Hu (neuronal antibody) was used to colocalize neural crest cells with neurons. Smooth muscle antibody(SMA) was used to identify the relation of the neural crest cells relative to the layers of the ureteral wall.
RESULTS: NCCs were present along the ureter and bladder (Figure 1). These cells colocalize with Hu+ ureteral neurons in all segments of the ureter (Figure 2), in both the submucosal and muscular compartments (Figure 2 and 3).
CONCLUSIONS: The autonomic nervous system of the ureter includes an intrinsic component that originates from the neural crest. These cells are present along the entire length of the ureter, are patterned in two concentric layers, and differentiate into Hu-expressing neurons. 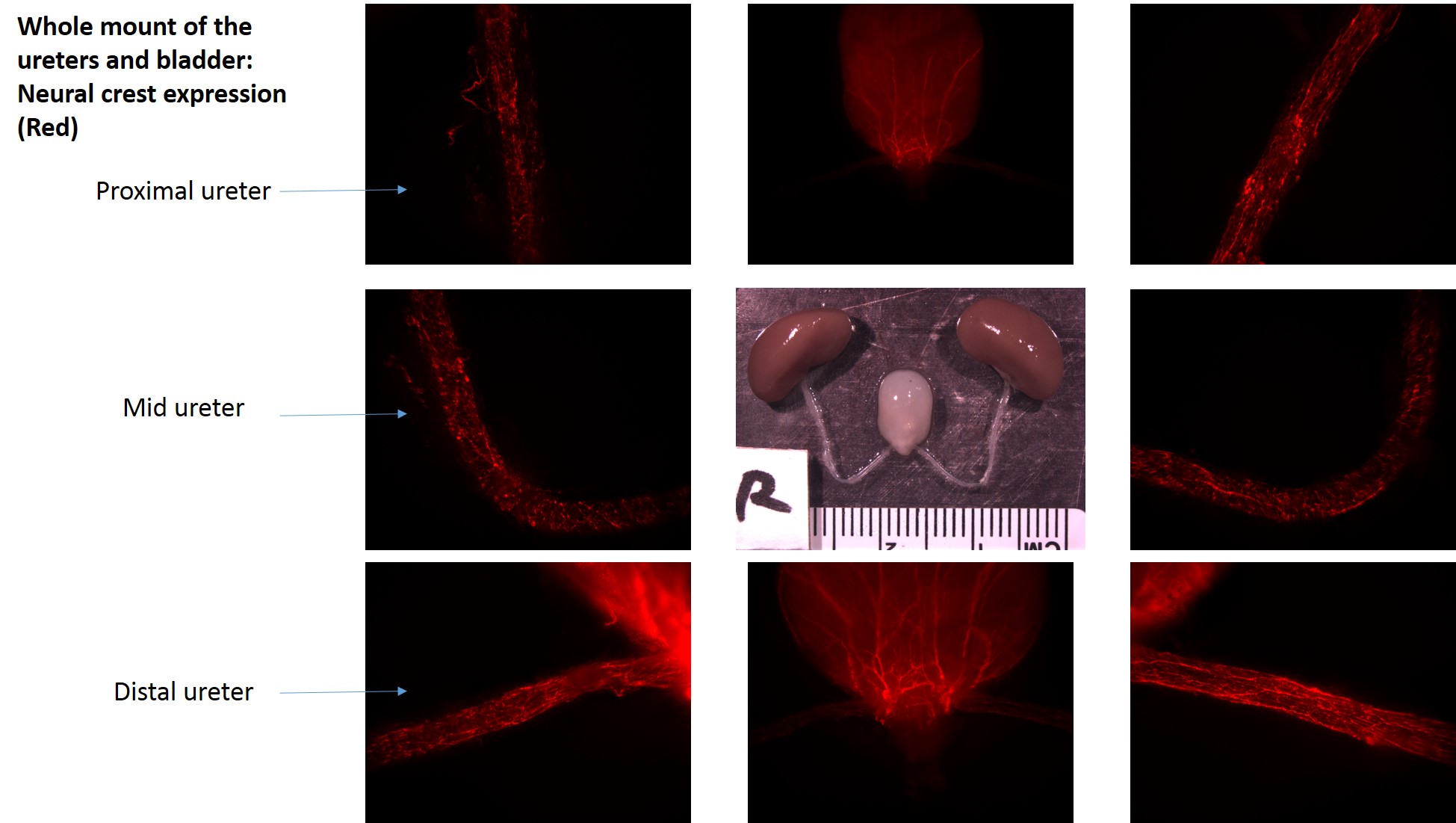
Back to 2018 Program
