Intravesical Docetaxel for the Management of High-Risk Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer (NMIBC) Following Failed BCG Therapy
Govind Shantharam, BA1; Jorge Pereira, MD1; Ohad Kott, MD2; Christopher Tucci, MS, RN2; Ali Amin, MD2; Anthony Mega, MD2; Dragan Golijanin, MD2; Boris Gershman, MD2
1Warren Alpert School of Medicine at Brown University, Providence, RI; 2Minimally Invasive Urology Institute, Providence, RI
Background: There are limited bladder-preserving therapeutic options for patients with high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) after failed intravesical bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) therapy. Salvage intravesical docetaxel therapy was originally described in 2006 but has not been validated outside of the original institution. In this study, we present the first external report on the oncologic outcomes of salvage intravesical docetaxel.
Methods: We identified 13 patients with high-risk NMIBC previously treated with one or more courses of intravesical BCG who received salvage intravesical docetaxel. Recurrence-free survival (RFS) was estimated using Kaplan-Meier method. Associations of clinicopathologic features with RFS were evaluated using univariable Cox regression.
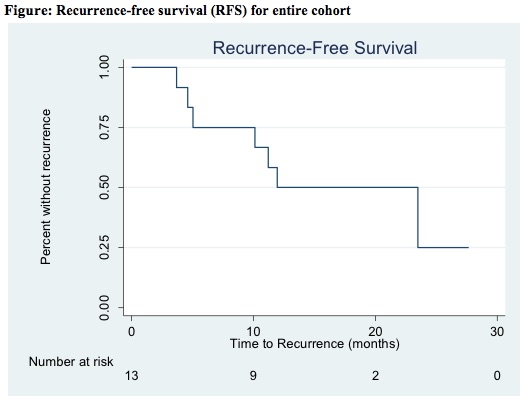
Results: Median age at pre-docetaxel recurrence was 75 (66, 78) years, and 46% of patients were male. 92% of patients had a prior diagnosis of high grade T1 disease, 39% had a prior diagnosis of CIS, and 46% had received 2 or more prior courses of BCG. Only 1 (8%) patient experienced docetaxel-related toxicity. Nine (69%) patients had a complete response at initial post-docetaxel cystoscopy. During a median follow-up of 12.0 (IQR 5.0, 18.1) months, a total of 7 (54%) patients developed recurrence (Figure). Median time to recurrence was 10.1 (IQR 4.6, 12.0) months. Estimated RFS at 6-, 12-, 18-, and 24-months was 75%, 50%, 50%, and 25%. Three (23%) patients ultimately underwent cystectomy. On univariable analysis, multiple courses of induction BCG was associated with decreased RFS, although did not reach statistical significance (HR 4.69, p=0.08).
Conclusions: In this first external validation study, intravesical docetaxel was associated with a 69% initial response rate and 50% RFS at 18-months among patients with high-risk NMIBC after failed BCG therapy.
Back to 2018 Program
