Back to 2025 Abstracts
Penelope: tissue penetration of gemcitabine phosphate metabolites following TAR-200 administration vs standard intravesical instillation in minipigs
David Cahn, MD1, Siamak Daneshmand, MD
2, Koen Wuyts, BS
3, Marc De Meulder, BS
3, Liesbeth Vereyken, BS
3, Marjolein van Heerden, DVM
3, Herman Borghys, DVM
3, Geert Mannens, PhD
3, Karen Daniel, PhD
4, Samuel Spigelman, MD
5.
1Colorado Urology, Lakewood, CO, USA, 2University of Southern California Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 3Janssen Research & Development, Beerse, Belgium, 4Janssen Research & Development, Lexington, MA, USA, 5Janssen Research & Development, Raritan, NJ, USA.
BACKGROUND: TAR-200 is a novel intravesical targeted releasing system designed to provide local continuous/sustained release of gemcitabine within the bladder, with potentially deep-tissue penetration. This preclinical study evaluated the penetration of gemcitabine (dFdC) and its active metabolites, diphosphate and triphosphate of dFdC (dFdCDP, dFdCTP), in bladder tissues up to 96 hours (h) after TAR-200 administration or intravesical instillation.
METHODS: Bladder tissue concentrations of gemcitabine and its active metabolites were measured in 5 minipigs following gemcitabine administration by intravesical or TAR-200 instillation. Three animals received a 2h bolus intravesical instillation with tissue collection from one animal at 2h, and 24h and 96h for the second and third, respectively. The TAR-200 system was placed into the bladder of two animals, until tissue collection at 48h and 96h, respectively. At necropsy, tissue samples were collected and the urothelium with underlying lamina propria were separated from the muscle layer of the urinary bladder.
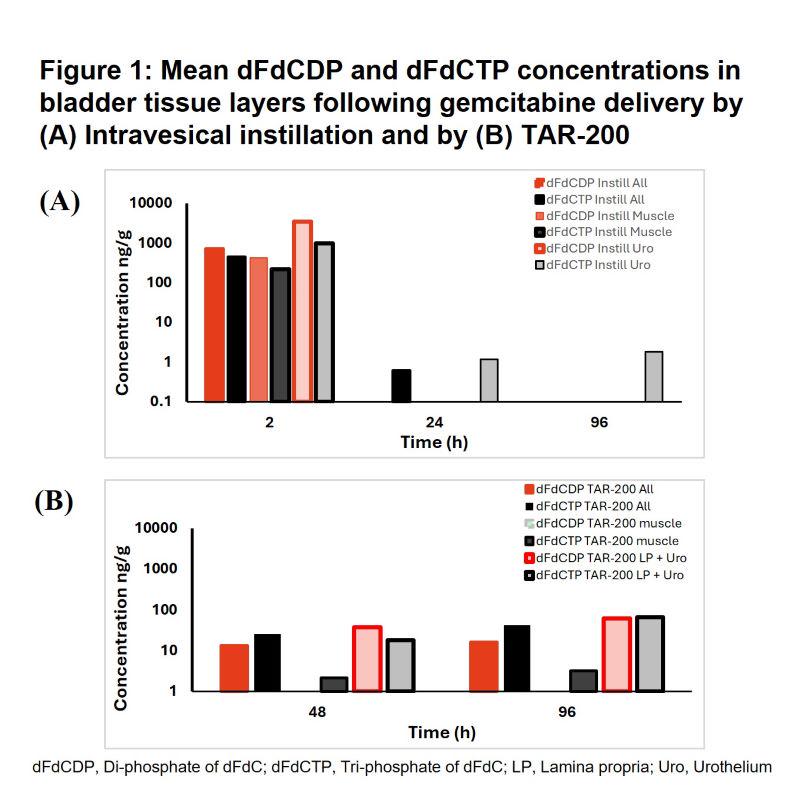
RESULTS: Following intravesical delivery of gemcitabine (2h), total bladder tissue concentrations of the active metabolites were high and detected in all bladder layers but were virtually undetectable in tissues samples after 24h and 96h (Figure 1A). When delivered with the TAR-200 system, gemcitabine active metabolites could be detected in all bladder layers over the investigated indwelling period up to 96h (Figure 1B).
CONCLUSIONS: Tissue exposure to gemcitabine delivered through a bolus instillation over a 2h indwelling period is limited by its short half-life (<3h) with little evidence of active metabolites in bladder tissue by 24h. Sustained local delivery of gemcitabine to the bladder through the TAR-200 system delivered active metabolites to all layers of the bladder at least 4 days following TAR-200 placement.
Back to 2025 Abstracts
