Back to 2025 Abstracts
Improving Postoperative Urologic Patient Care: Encouraging Language Diversity Through Implementation of Language Concordant Discharge Instructions
Daniela Diaz Rubayo, MD,
Justin V. Nguyen, BS, Katherine Merport, BA, Jennifer E. Fantasia, MD.
UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA.
BACKGROUND: Written postoperative discharge instructions are important for high-quality patient care. However, language concordant instructions (LCI) for patients with limited English proficiency are often unavailable which can impact access, quality, and satisfaction with care. This QI project aims to address this language barrier by providing LCI for urology patients.
METHODS: Spanish, Portuguese, and Albanian are the most common non-English languages in this patient population. Translation services helped create standardized LCI in these languages for common urologic procedures. LCI were shared with the entire urology department in May 2023 via Epic SmartPhrases. A retrospective chart review was performed from 12/1/2022 to 12/31/2023. Patients were identified through CPT codes for procedures with applicable LCI and divided into English and non-English groups. The number of patients receiving LCI pre-intervention (12/1/2022 - 5/31/2023) and post-intervention (6/1/2023 - 12/31/2023) was compared using a chi-squared test.
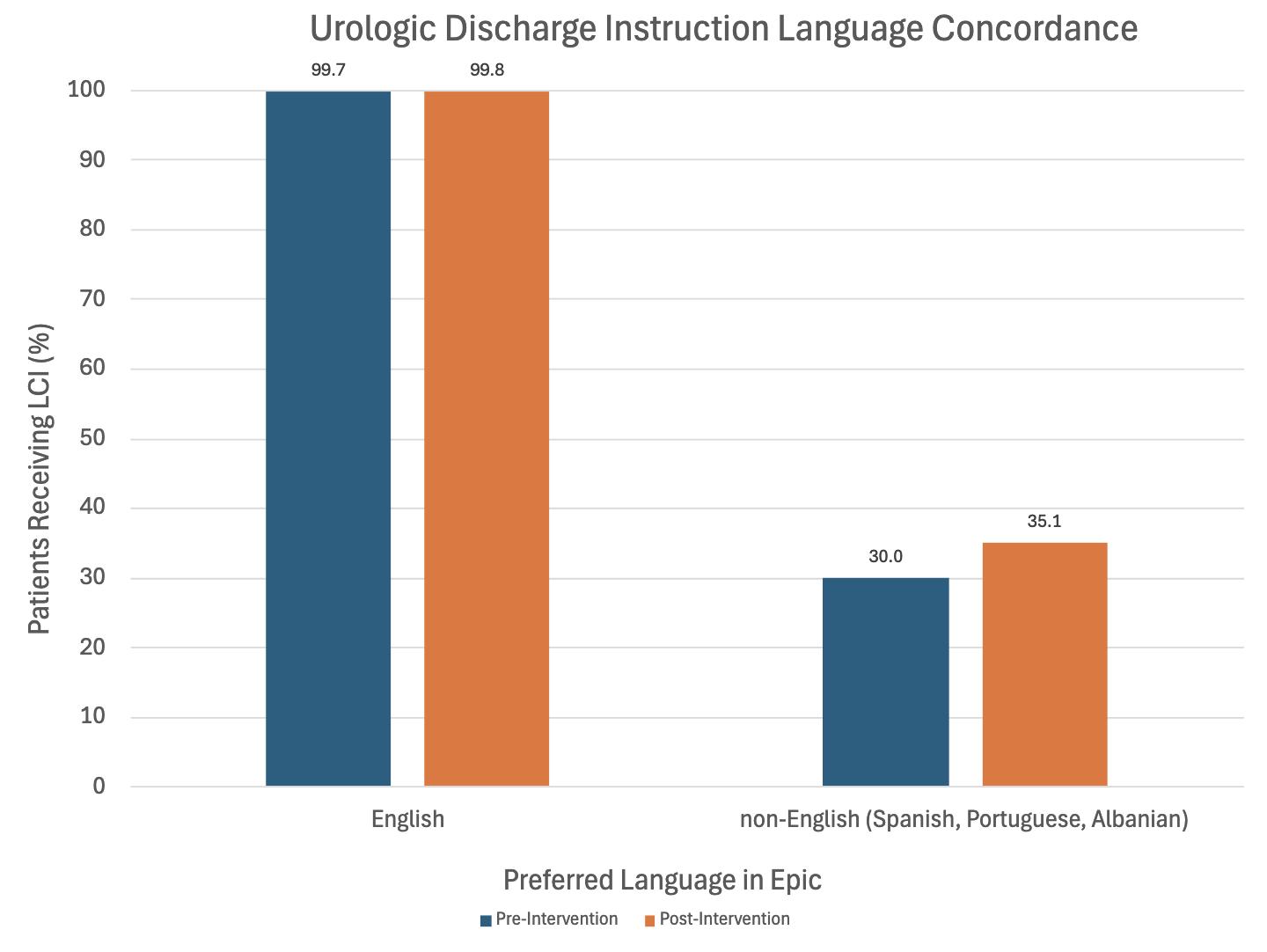
RESULTS: A total of 1324 English (pre-intervention: 643, post-intervention: 681) and 137 non-English (pre-intervention: 40, post-intervention: 97) speaking patients were identified. In the non-English group, 34 patients received LCI post-intervention compared to 12 patients pre-intervention, however this improvement was not statistically significant (p = 0.6). Serving as a control, there was no statistically significant difference pre- and post-intervention in the English group (p = 0.5). Figure 1 illustrates the percentage of patients receiving LCI.
CONCLUSIONS: Although there was no statistically significant difference, more non-English-speaking patients received LCI post-intervention. This initial effort highlights an accessible intervention to improve equitable patient care. Next steps to improve LCI utilization in the urology department include healthcare provider education and awareness campaigns. Future studies are needed to assess the impact of LCI in postoperative outcomes and patient experience.
Back to 2025 Abstracts
