Back to 2025 Abstracts
ERAS and Beyond: Optimizing Radical Cystectomy Outcomes with Modified ERAS
Adam Cole, MD1, Joshua Linscott, MD, PhD
2, Connor Pelletier, BS
3, Evelyn James, MPH
1, Erin Santos, PA, MPH
1, Jeffrey Howard, MD, PhD
1, Stephen Ryan, MD
1, Matthew Hayn, MD
1, Jesse Sammon, DO
1, Randie White, MD
1.
1Maine Medical Center, Portland, ME, USA,
2Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, FL, USA,
3University of New England, Portland, ME, USA.
BACKGROUND: Radical cystectomy (RC) carries a high risk of complications, leading to the adoption of Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocols. At our institution, ERAS implementation in 2020 did not reduce post-operative complications, prompting modifications to our perioperative pathway. We assessed whether a modified ERAS protocol (M-ERAS) reduced complications and readmissions.
METHODS: Starting April 1, 2022, we introduced M-ERAS, adding the following to preexisting ERAS protocols: oral prophylactic anticoagulation, nurse follow-up calls on post-discharge days 2 and 5, enhanced pre-op education, and low-dose antibiotic prophylaxis (Levofloxacin or Bactrim from POD4 until stent removal) based on an RC-specific antibiogram. We analyzed 306 RC patients with ileal conduit (2015-2024) and 90-day follow-up. Outcomes of 232 ERAS patients were compared to 74 M-ERAS patients using multivariable logistic regression.
RESULTS: Groups had no significant differences in demographics, neoadjuvant status, or comorbidities. Among ERAS patients, 417 complications occurred (74.5% within 30 days), primarily infectious (27.3%), GI (17.3%), and GU (12.2%) (Figure 1). In the M-ERAS cohort, 119 complications were recorded (67.2% within 30 days), with GI (27.7%), infectious (19.3%), and wound-related (13.4%) being most common (Figure 1). The 30-day GU infection rate dropped from 48.3% to 21.4% (p = .002, Table 1). M-ERAS was independently associated with a lower risk of GU infection at 30 and 90 days.
CONCLUSIONS: Modifying ERAS protocols significantly reduced complications, particularly GU infections, and readmissions following RC.
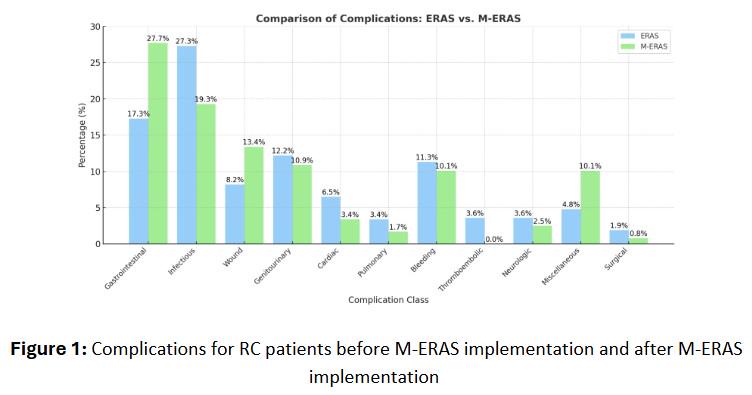
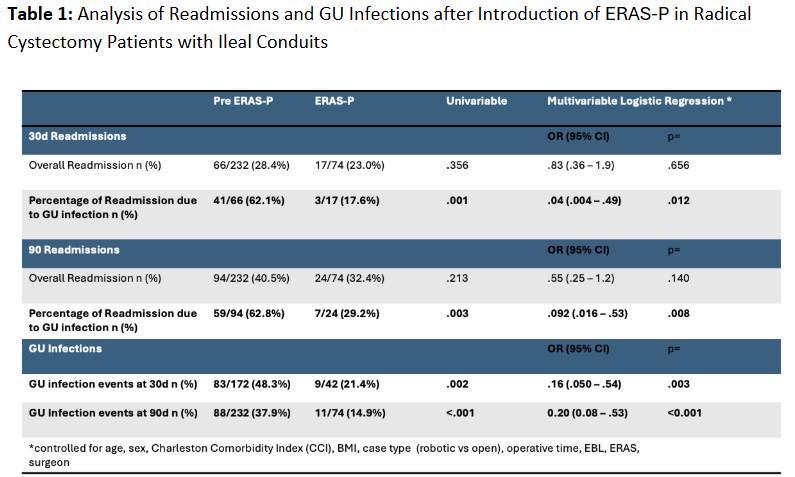
Back to 2025 Abstracts

