Back to 2025 Abstracts
Comparative Analysis of PI-RADS and PI-FAB Scoring Systems in Post-Focal Therapy Assessment of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Nethusan Sivanesan, BS, Gabriela M. Diaz, MD, Wei S. Tan, MD, PhD, Sandeep Arora, MBBS, Preston C. Sprenkle, MD.
Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA.
BACKGROUND: Accurate assessment of post-focal therapy (FT) imaging is essential for the detection of recurrent clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa). While the Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) is commonly used for treatment naive prostate lesion identification, its effectiveness in post-FT assessment is limited. The new Prostate Imaging after Focal Ablation (PI-FAB) system may provide better diagnostic performance. In this study we compare the diagnostic abilities of PI-RADS and PI-FAB in detecting csPCa following FT.
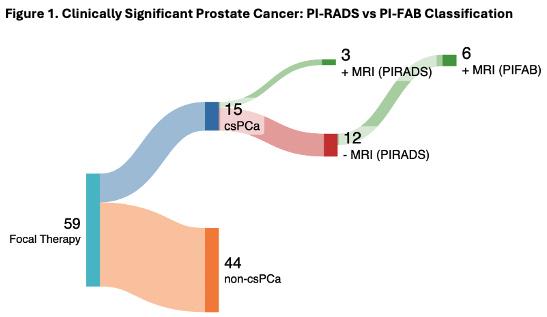
METHODS:We retrospectively analyzed 59 patients who underwent FT (cryotherapy, NanoKnife, TULSA), post-treatment mpMRI, and subsequent prostate biopsy. Mandatory biopsy at one-year identified 15 patients with csPCa. For this sub-cohort, a genitourinary radiologist was blinded and prospectively evaluated the mpMRI scans using the PI-FAB system. PI-RADS scores were retrieved retrospectively. Sensitivity was calculated using biopsy-recommended thresholds: PI-FAB score of 3 (range 1-3) and PI-RADS scores of 4-5 (range 1-5), representing high-risk categories in each system.
RESULTS: Of the 59 patients, 15 patients (25.4%) had csPCa at one year biopsy post-FT. Among those, PI-RADS identified csPCa only in 3 of 15 cases (20%). When applying PI-FAB, 9 of 15 (60%) csPCa patients were accurately identified (Figure 1). PI-FAB demonstrated a higher sensitivity compared to PI-RADS (60% vs 20%), indicating that PI-FAB is more effective in identifying patients with csPCa following focal therapy.
CONCLUSIONS:PI-FAB demonstrated higher sensitivity than PI-RADS for detecting csPCa post-focal therapy, suggesting improved accuracy in identifying residual or recurrent disease. However, it is important to appreciate that 40% of patients with csPCa are still missed despite the use of PI-FAB highlighting limitations of MRI imaging alone for post-FT surveillance.
Back to 2025 Abstracts
