Back to 2025 Abstracts
Evaluating The Therapeutic Role of Lymph Node Dissection in Variant Subtype Bladder Cancer
Syed N. Rahman, MD1, Darryl Martin, MD
1, Wei Shen Tan, MD
1, David Hesse, MD
1, Peter Humphrey, MD
1, Jonathan Wright, MD
2, Sunil Patel, MD
3, Fed Ghali, MD
1.
1Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, USA,
2University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA,
3Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, USA.
BACKGROUND:The importance of lymph node dissection (LND) at time of radical cystectomy for urothelial carcinoma (UC) is widely accepted despite known risks. Therapeutic benefits of LND for variant subtype bladder cancer (VBC), a heterogenous and distinct set of diseases, are not well established.
METHODS:The National Cancer Database was queried for all cases of variant subtype bladder cancers using International Classification of Disease-O-3 morphologic codes managed with radical cystectomy between 2004 and 2020. Cases were stratified by variant subtypes. Primary outcome was overall survival associated pathologic nodal status and receipt of nodal dissection. Kaplan Meier analysis and Cox proportional hazards analysis were used for survival analyses.
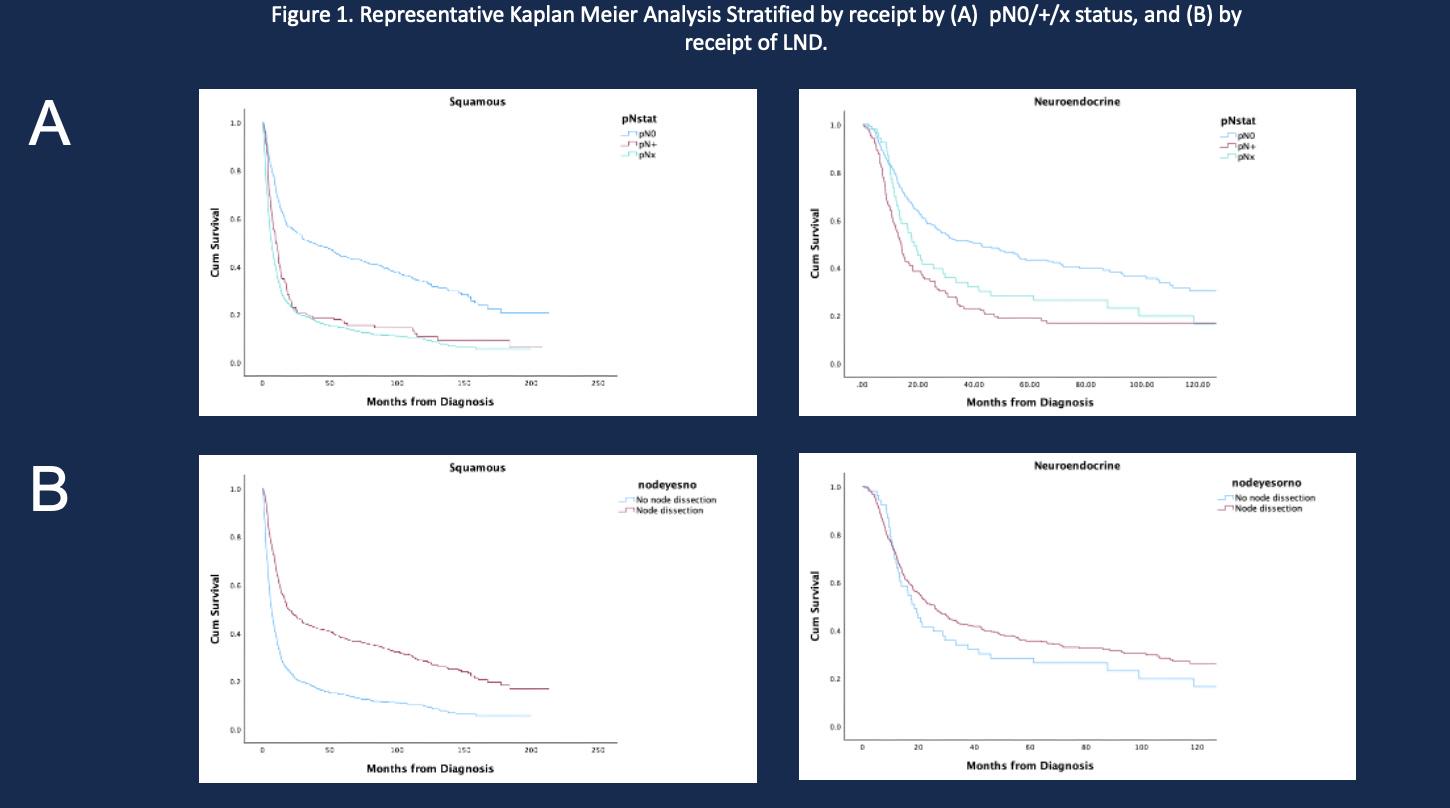
RESULTS: A total of 30,911 patients with VBC were included in our analysis that were managed with radical cystectomy. pNx rates ranged from 33.1% in the micropapillary subtype, 42.2% in the sarcomatoid subtype, 68.4% in the squamous subtype, 48.9% in the adenocarcinoma subtype, 56.2% in the neuroendocrine subtype. Median OS was higher in those that received a nodal dissection across subtypes, but was statistically significant only squamous (71.0 [68.0 vs. 74.0] vs. 37.2 [33.6 vs. 40.9] months p<0.001) and adenocarcinoma (45.9 [32.9 vs. 59.0] vs. 37.9 [28.6 vs. 47.1] months p=0.037). Using Cox proportional hazards regression, LN dissection was associated improved OS for squamous (0.50 (0.44-0.58) p<0.001) and adenocarcinoma (0.68 [0.45-0.91) p=0.035).
CONCLUSIONS:The role of LND across VBC subtypes is not clearly defined and warrants further investigation to develop a more risk-adaptive approach. We demonstrate heterogeneity with respect to the OS benefit associated with LND. Among certain VBC subtypes, LND may not offer significant therapeutic benefit, while LND in squamous and adenocarcinoma VBC is correlated with improved survival.
Back to 2025 Abstracts
