Back to 2025 Abstracts
Real-World Outcomes of Chemoradiation Therapy for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer inOlder Adults
Piroz Bahar, B.A.1, Agustin Perez, M.D.
2, Sumedh Kaul, MS
2, Jason Efstathiou, MD
3, Stephen Williams, MD
4, Yong Shan, PhD
4, Peter Chang, MD
2, Andrew Wagner, MD
2, Aaron Fleishman, MPH
2, Aria Olumi, MD
2, Boris Gershman, MD
2.
1University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, MI, USA,
2Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA, USA,
3Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, USA,
4University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX, USA.
BACKGROUND: Chemoradiation therapy (CRT) represents a bladder-preserving alternative to radical cystectomy (RC). While seminal studies have reported comparable 5-year cancer-specific (CSS) and overall survival (OS) to RC, these data reflect high-volume academic center experiences. We, therefore, emulated a real-world, single-arm trial in older adults based on the control arm of SWOG/NRG 1806.
METHODS: Using SEER-Medicare data, we included adults 66-89 years with T2-T4aN0M0 bladder cancer treated with radiation and concurrent chemotherapy (cisplatin, gemcitabine, or 5-FU+mitomycin C) from 2000-2017. We examined bladder-intact survival, CSS, and OS using the Kaplan-Meier method. Associations of baseline characteristics with cancer-specific mortality (CSM) were evaluated using Cox regression.
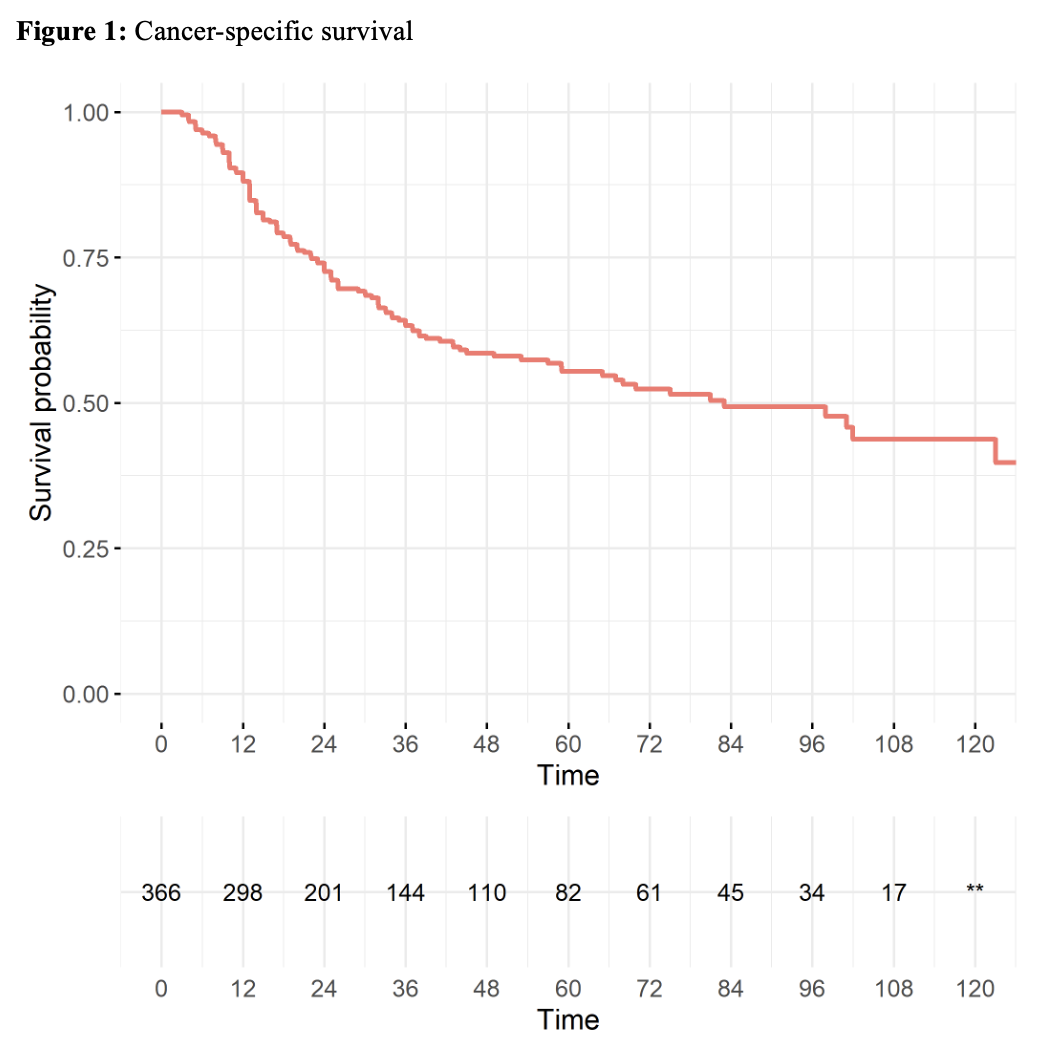
RESULTS: A total of 367 patients were included. Median age was 78 years (IQR 73-82). Tumor stage was T2 in 321 (87%). Median follow-up was 27.0 months. At 5-years, bladder-intact survival was 49%, CSS was 55%, and OS was 36% (Figure 1). On univariable analysis, female gender (HR 1.61) and Black race (HR 2.14) were associated with increased risk of CSM, while higher zip code income (unit HR 0.35 per $100,000) and higher education level were associated with lower risk of CSM. On multivariable analysis, female gender (HR 1.47) was associated with increased risk of CSM, while higher education level (HR 0.41 for <14% without high school education versus >29%) was associated with reduced CSM.
CONCLUSIONS: Notwithstanding the limitations of SEER-Medicare, in observational analyses designed to emulate a target trial, real-world CRT was associated with lower CSS and OS than reported in seminal trials. Additional studies are required to determine if this is related to the efficacy of CRT in real-world settings or differences between trial and non-trial populations.
Back to 2025 Abstracts
