Back to 2025 Abstracts
Baseline renal function influences overall survival in patients undergoing renal mass ablation of small renal masses
Borivoj Golijanin, MD1, Raymond Che, BSc
1, Richard Glebocki, BSc
1, Kamil Malshy, MD
1, Aaron Seto, BSc
1, Brian Jay, MD
2, Emily Barry, MD
1, Scott Collins, RT(R)(CT)
2, Aaron Maxwell, MD
2, Gregory Dubel, MD
2, Sari Khaleel, MD
1, Dragan Golijanin, MD
1.
1Minimally Invasive Urology Institute, Brown University Health, Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI, USA,
2Brown University Health, Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI, USA.
BACKGROUND: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a common feature in patients with renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and it can affect management options and prognosis, making nephron-sparing approaches, such as renal mass ablation (RMA), favorable when possible. In this study, we evaluate survival of patients with RCC and varying degrees of CKD who underwent RMA.
METHODS: Consecutive patients undergoing RMA at a tertiary care center were retrospectively reviewed. Records were grouped based on baseline renal function as CKD1-2, CKD3a-3b, and CKD4-5. Kaplan-Meier (KM) was used to evaluate OS in each group. Influence of post-ablation changes in CKD status was evaluated.
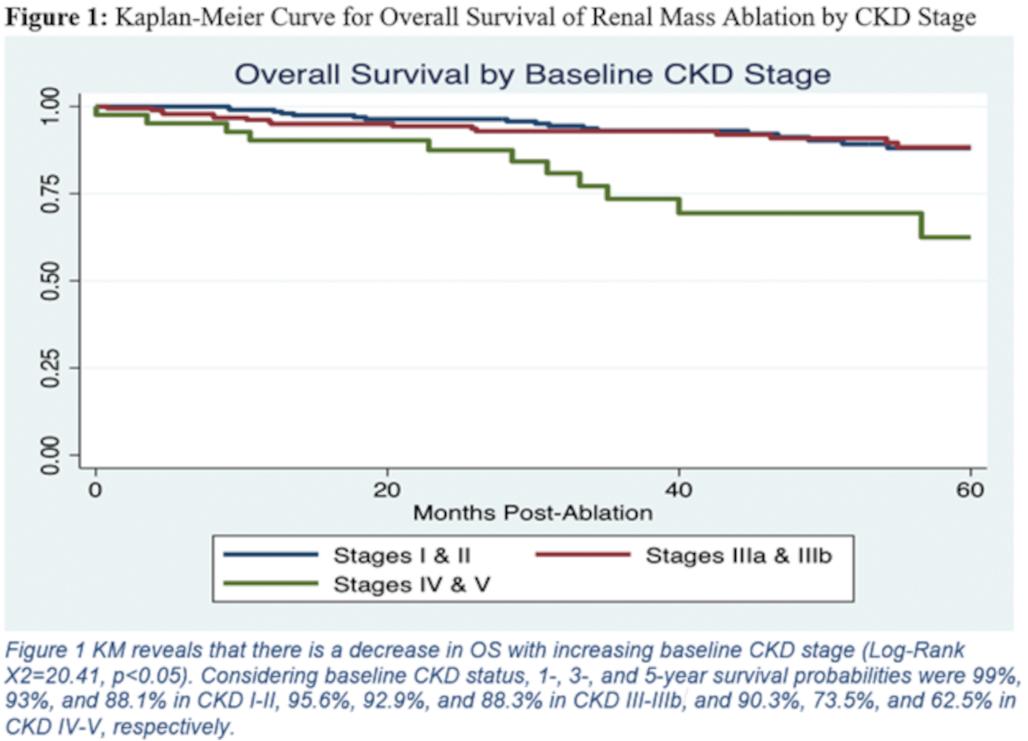
RESULTS: Of 459 patients, 48% were CKD I-II at baseline with median follow-up of 47.6 months, 43% with CKD IIIa-IIIb with median follow-up of 45.1 months, and 9% with CKD IV-V with median follow-up 46.9 months. KM reveals that there is a decrease in OS with increasing baseline CKD stage (Log-Rank
Χ2=20.41, p<0.05). Considering baseline CKD status, 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival probabilities were 99%, 93%, and 88.1% in CKD I-II, 95.6%, 92.9%, and 88.3% in CKD IIIa-IIIb, and 90.3%, 73.5%, and 62.5% in CKD IV-V, respectively (
Figure 1). Post-ablative changes in CKD status did not significantly influence mortality (RR=1.57, 95%CI=0.9029-2.7349, z=1.59, p=0.11).
CONCLUSIONS: Pre-ablation renal function is a predictor of OS in patients undergoing RMA for their SRM. Poor renal function, specifically CKD4-CKD5, is associated with a significant drop in survival after 1-year. Post-ablative changes in CKD status in the first 5-years after RMA do not affect mortality risk. These findings can influence counseling for patients with CKD who are considering RMA.
Back to 2025 Abstracts
