Back to 2025 Abstracts
The Role of CRP in Cystectomy: Forecasting Future Complications
Adam Cole, MD1, Randie White, MD
1, Raeann Dalton, DO
1, Connor Pelletier, BS
2, Emilie Platteter, BS
2, Evelyn James, MPH
1, Joshua Linscott, MD, PhD
3, Jeffrey Howard, MD, PhD
1, Stephen Ryan, MD
1, Matthew Hayn, MD
1, Jesse Sammon, DO
1.
1Maine Medical Center, Portland, ME, USA,
2University of New England, Portland, ME, USA,
3Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, FL, USA.
BACKGROUND: Radical cystectomy (RC) is a procedure with significant complications, including infections, wound complications, or anastomotic leaks (I/W/L). Identifying high-risk patients is crucial for morbidity reduction. C-reactive protein (CRP), a non-specific inflammatory marker, is often used postoperatively. We hypothesized that an elevated CRP on post-op day (POD) 4 could signal an increased risk of I/W/L complications.
METHODS: We analyzed 153 consecutive RC patients from a prospectively maintained database, each with a single POD#4 CRP. Leukocytosis (WBC >11.0) from POD#3 until discharge was recorded. Complications were classified using the MSKCC grading system. Patients with I/W/L complications within 14 days were compared to those without. Receiver operating characteristic analysis and Youden’s Index determined a CRP cutoff for predicting complications. Multivariable analysis assessed independent risk factors.
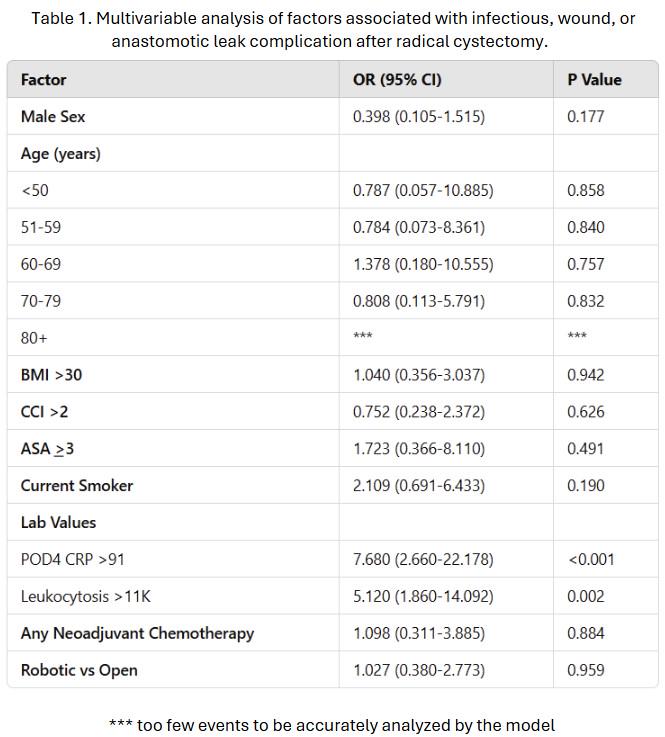
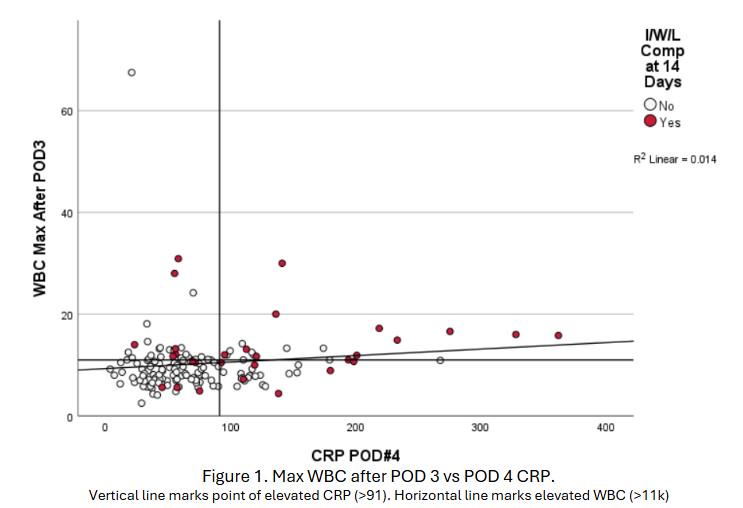
RESULTS: No significant demographic differences between groups were found (Table 1). CRP was strongly predictive (AUC = 0.762), with a calculated cutoff of 91. CRP >91 (OR 7.68, 95% CI 2.6-22.18, p<0.001) and leukocytosis (OR 5.1, 95% CI 1.86-14.09, p=0.002) were independently associated with I/W/L complications (Table 1). CRP and WBC showed no significant correlation (R = 0.118) (Figure 1). A CRP of >90 was predictive of a complication in the robotic group compared to a CRP > 118 in the open group, however not significantly (p=0.432).
CONCLUSIONS: An elevated CRP on POD#4 is an independent predictor of I/W/L complications post-RC, even without leukocytosis. CRP provides additional prognostic value alongside WBC. Patients with high CRP may require closer monitoring or modified discharge planning to reduce morbidity.
Back to 2025 Abstracts

