Back to 2025 Abstracts
Radiation Cystitis Associated Patient Reported Outcomes and Urine Inflammatory Biomarkers Pre and Post Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Ambrose Orr, MD1, Richard Bellemare, MD
1, Daniel Mielcarz, PhD
2, Suwen Wu, MS
3, Janet Peacock, BS
3, Pamela Hannigan, RN
1, Lawrence Bornt, RN
1, William Bihrle, III, MD
1, Jay Buckey, Jr., MD
4, Rachel A. Moses, MD, MPH
1.
1Dartmouth Health Department of Surgery, Section of Urology, Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Lebanon, NH, USA,
2DartLab Dartmouth Cancer Center Geisel School of Medicine, Hanover, NH, USA,
3Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth College, Hanover, NH, USA,
4Dartmouth Health Department of Medicine, Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Lebanon, NH, USA.
BACKGROUND: Hyperbaric Oxygen (HBO2) therapy is used to treat radiation cystitis (RC) however, validated objective efficacy measures are needed. This study explored urinary symptoms and inflammatory biomarkers in patients with RC undergoing HBO2.
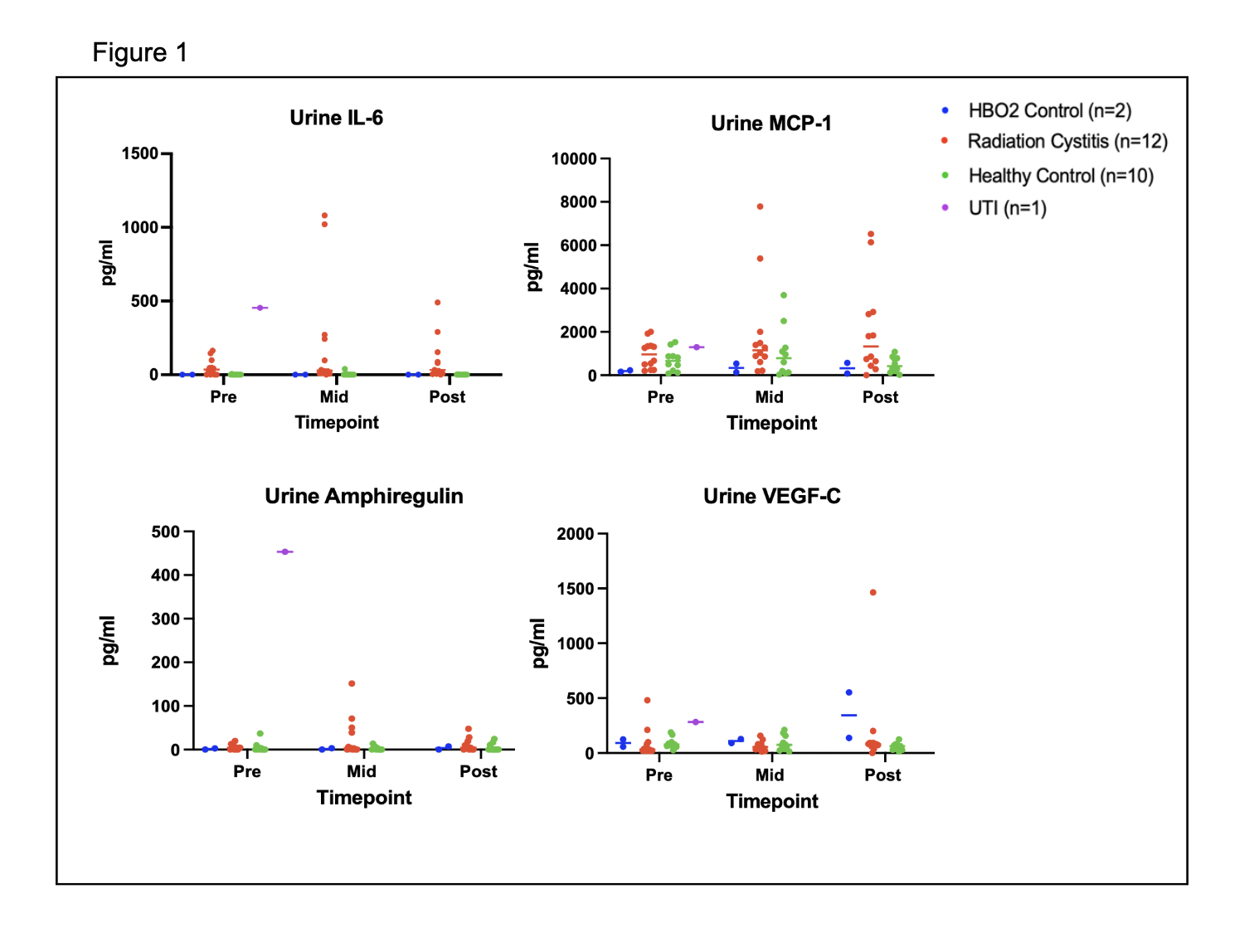
METHODS: Adult patients with Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) ≥ grade 3 RC and control patients were recruited. Pre-post patient reported hematuria and results were collected and compared. Mid-stream morning non-infected urine were collected within one week of the first, middle and last HBO2 treatment for RC samples and at three similar time points for controls. A priori urinary biomarker analysis (Luminex multiplex assay), normalized with creatinine concentration, focused on interleukin-6 (IL-6), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), amphiregulin, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-C). Questionnaire results were compared using paired statistics. Biomarkers were analyzed using a linear mixed effect model.
RESULTS: In total, 24 patients, age 73 (SDą3) met inclusion criteria. Twelve had RC following prostate cancer treatment (mean 49 HBO2 treatments). The controls included 8 healthy controls and 2 who received HBO2 for other conditions. Patient reported gross hematuria (2.4 to 0.5, p<0.01) improved post HBO2. Both IL-6 and MCP-1 were significantly lower in the controls. MCP-1 increased significantly over time (p=.04) and showed a significant group/time interaction with a greater increase in the cystitis group (p=0.04). IL-6 showed a trend toward an increase over time (p=0.07) with a greater increase in the cystitis group (p=0.08).
CONCLUSIONS: Participants with RC demonstrate resolution of gross hematuria scores post HBO2. IL-6 and MCP-1 may be unique urine biomarkers to follow HBO2 outcomes.
Back to 2025 Abstracts
