|
Back to 2015 Joint Annual Meeting
Self-Reported Physical Activity and its Effect on Female Sexual Dysfunction
Stanley Zaslau, Dale Riggs, Barbara Jackson, Henry Fooks, Chad Morley, Morris Jessop, Randy Bryner, Stanley Kandzari
West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV
Introduction: To evaluate the effect of physical activity on Female
Sexual Dysfunction (FSD), we report on 110 female subjects who completed a self-reported physical activity questionnaire in addition to the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI).
Materials & Methods: The survey was administered to female patients being seen in the general Urology clinics at West Virginia University. Domain values (desire, arousal, lubrication, orgasm, satisfaction, and pain) were obtained by using the FSFI. Additionally, self-reported leisure time physical activity was
measured by the Godin Leisure-Time Physical Activity Questionnaire and those scores grouped into 3 domains (Low, Moderate and High).
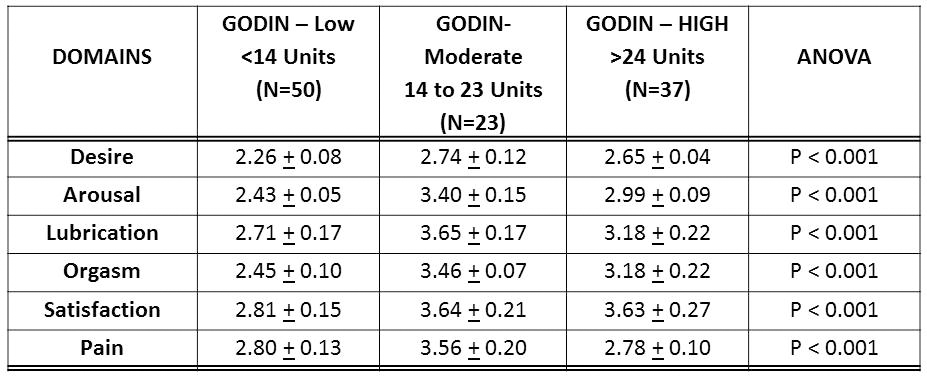
Results: Moderate amounts of physical activity significantly improved (P< 0.001) Desire, Arousal, Lubrication and Orgasm compared to both Low and High Godin levels. There was no improvement in Satisfaction between the Moderate and High Godin levels, but both were significantly increased when compared to Low Godin Level (P< 0.001). Pain was significantly improved by Moderate amounts of physical activity compared to both Low and High Godin levels (P< 0.001).
Conclusions: Subjects who self-reported moderate levels of
activity as measured by the Godin Leisure-Time Physical Activity Questionnaire exhibited significant improvement in the FSFI domains of Desire, Arousal, Lubrication and Orgasm. Further investigation into the effects of exercise and increased
physical activity is a source of ongoing investigation.
Back to 2015 Joint Annual Meeting
|

