|
|
 |
Back to Annual Meeting Program
Human Fatty Acid Synthase: Potential as Novel Serum Biomarker for Prostate Cancer
Ramdev Konijeti, M.D.1, Cornelia Photopoulos, B.S.1, Mohan Brahmandam, Ph.D.1, Adam Kibel, M.D.2, Massimo Loda, M.D.1.
1Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA, USA, 2Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA, USA.
Fatty acid synthase (FASN) is a multi-enzyme complex that plays a crucial role in fatty acid synthesis. Our group has previously shown that FASN tissue expression in radical prostatectomy specimens correlates with progression of prostate cancer (CaP) from normal to prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) to metastasis, independent of Gleason grade. The FAS-detect™ enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) by FASgen® is a novel sandwich ELISA that can be used to quantitate soluble FASN. We hypothesized this assay could accurately detect soluble FASN and could be used to quantify FASN in the lysates and in the media of cultured benign epithelial and prostate carcinoma cells.
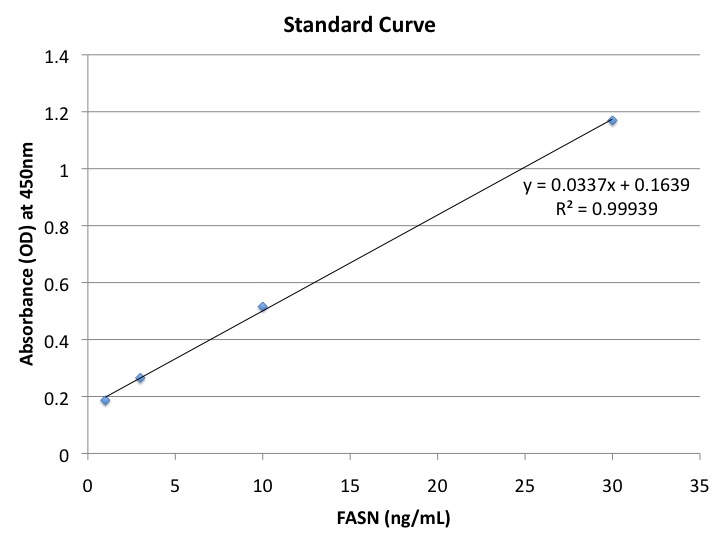
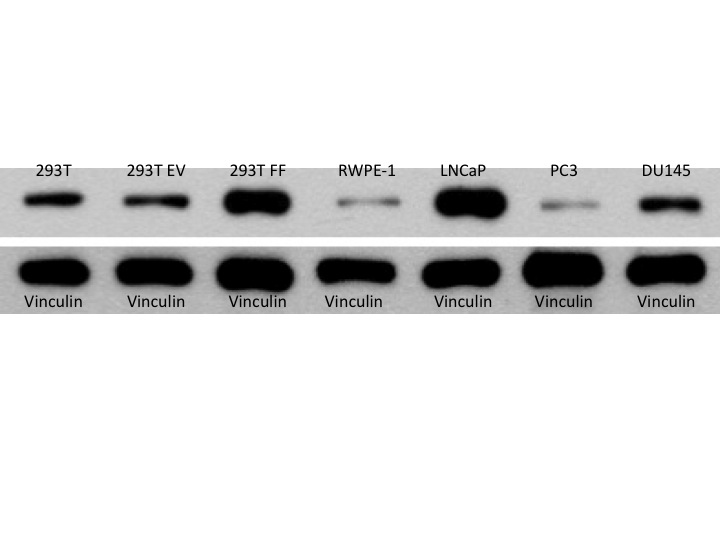
Purified FASN was obtained by affinity purification of lysates of cultured benign human embryonic kidney cells (293T) cotransfected with FLAG-FASN. Purification was confirmed by Coomassie stain. Purified FASN were loaded in separate wells (0 ng/mL, 5 ng/mL, 10 ng/mL, and 30 ng/mL, respectively) into the ELISA to generate a standard curve (Figure 1). Assay results were obtained using a spectrophotometer to determine optical density at 450nm. Linear regression was performed to determine the R2 coefficient. 293T, 293T cotransfected with the empty vector and FLAG-FASN (293T EV and 293T FF, respectively) (pcDNA™ 3.1-FLAG-A backbone by Invitrogen™), benign prostate epithelial (RWPE-1), and prostate carcinoma (LNCaP, PC3, DU145) cells were grown in culture to >70% confluence. FASN expression in lysates and culture media was determined by both Western blot and ELISA (Figures 2 & 3). All ELISA samples, including standards, were assayed in duplicate.
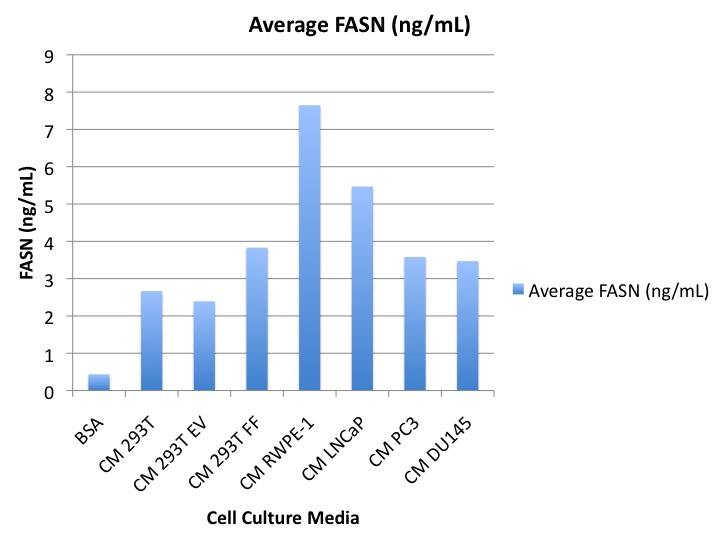
LNCaP cell lysate expressed the highest concentration of FASN with an average of 256 ng/mL, in contrast to PC3 cells, which expressed the lowest concentration of FASN with an average of 26 ng/mL. 293T, 293T EV, and 293T FF cells expressed average FASN concentrations of 58 ng/mL, 66 ng/mL, and 87 ng/mL respectively (Figures 2 and 3). Media of cultured cells consistently expressed detectable concentrations of FASN (Figure 4).
FAS-detect™ ELISA can accurately and reproducibly detect low levels of soluble FASN. Furthermore, consistent expression of extracellular FASN, as detected in the media of cultured prostate carcinoma cells, illustrates the potential of using circulating FASN as a surrogate for tissue FASN, and therefore aggressive prostate cancer. Further studies of the biology of extracellular FASN and assays of serum from individuals with CaP are warranted.
Back to Annual Meeting Program
|