|
Back to Annual Meeting Program
Robotic Assisted Radical Prostatectomy for High Risk Prostate Cancer: Quality of Life Outcomes in Men Who Elect Surgery as Primary Therapy
Hoyt Doak, MD1, Ryan Dorin, MD2, Halil Kiziloz, MD2, Joseph Wagner, MD2.
1University of Connecticut, Farmington, CT, USA, 2Hartford Specialists, Hartford, CT, USA.
BACKGROUND:
Robot assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) with pelvic lymph node dissection is increasingly performed on patients with high-risk prostate cancer. There are few studies on quality of life (QOL) outcomes following RARP for high-risk disease. We used a validated QOL questionnaire to evaluate of the long-term morbidity associated with this treatment paradigm.
METHODS:
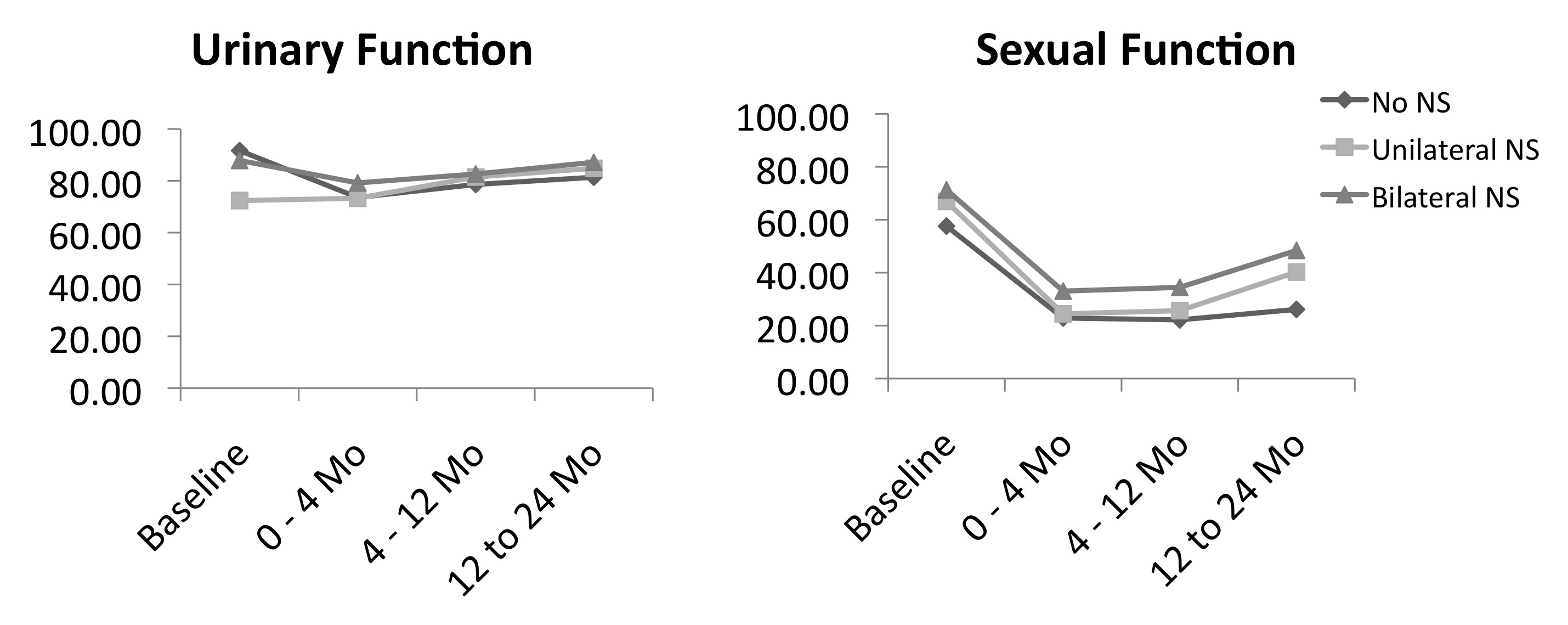
Men included in our institutional IRB approved prostatectomy database are asked to complete the Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite (EPIC-26) questionnaire preoperatively and at each follow-up visit. We queried the database for all patients who underwent RARP as initial therapy for D’Amico high-risk prostate cancer between 2/2004-11/2011. Patients were excluded if they had undergone previous radiotherapy or androgen deprivation therapy. Questionnaire scores were aggregated into a composite index score of 0-100, with 100 representing the most favorable score for the following domains: urinary function (UF), bowel health (BH), hormonal function (HF), and sexual function (SF). Index scores were stratified by nerve-sparing (NS) status. Linear regression models and analysis of variance were used for statistical comparisons.
RESULTS:
A total of 277 patients met inclusion criteria. Median age at surgery was 62; median follow-up interval was 11.7 months (max: 145 months); and a mean of 4.4 questionnaires were completed per patient. Eighty-one men underwent a bilateral NS procedure, 81 a unilateral NS procedure, and 115 a non-NS procedure.
Mean index scores on the UF, HF, and SF domains changed significantly from baseline (p<0.01 for all), while mean index scores on the BH domain did not change significantly (p=0.234). At 2 years, nerve-sparing status was associated with a statistically significant improvement in scores in the SF domain only, with patients undergoing unilateral (p=0.01) or bilateral NS (p<0.01) reporting higher scores than non-NS patients.
CONCLUSIONS:
QOL outcomes based on EPIC-26 scores for patients undergoing RARP for high-risk prostate cancer were similar to those of lower-risk cohorts in previously published studies. Randomized comparisons of QOL outcomes between treatment modalities for high-risk patients are needed to optimize treatment strategies.
Back to Annual Meeting Program
|