|
|
 |
Back to Annual Meeting Program
Robotic Urologic Surgery in the Elderly: Is There an Increased Risk of Complications?
Kristen R. Scarpato, MD1, Kyle T. Finnegan, BS2, Halil Kiziloz, MD2, Ryan P. Dorin, MD2, Anoop M. Meraney, MD2, Steven J. Shichman, MD2, Joseph R. Wagner, MD2, Stuart S. Kesler, MD2.
1University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington, CT, USA, 2Hartford Hospital, Hartford, CT, USA.
BACKGROUND: Elderly patients are increasingly referred for robotic surgical procedures. Robotic surgery has been associated with decreased perioperative morbidity, but concerns remain regarding trendelenberg positioning and prolonged pneumoperitoneum in this population.
METHODS: A single institution, prospectively managed database of patients undergoing robotic urologic surgery from 2005 to 2012 was reviewed. Patients ≥ 75 years of age undergoing partial nephrectomy (PN), radical cystectomy (RC), radical prostatectomy (RP), or upper tract reconstructions were included. Patient characteristics including age, sex, body mass index (BMI), and American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) score, as well as surgery type, length of stay (LOS), and estimated blood loss (EBL) were recorded. Early postoperative complications were reviewed and graded according to the 2004 Clavien System. Complication rates were compared to a younger cohort (< 75 years of age) at the same institution.
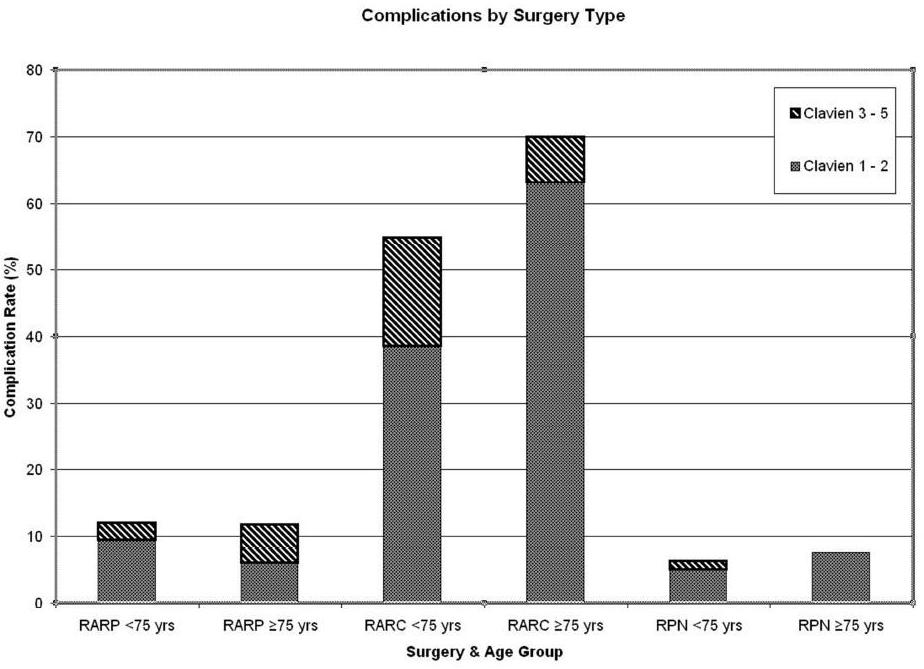
RESULTS: Seventy-nine patients underwent 82 robotic surgeries during the study period, including 39 PN, 20 RC, 17 RP, and 6 reconstructive procedures. Mean age at surgery was 77.8 years, mean BMI was 26.5, with a median ASA of 3. Mean LOS and EBL were 4.8 days and 333 ml, respectively. Major complications, all Clavien 3, occurred in 3 patients, and there were 26 minor complications in 19 patients for an overall complication rate of 23%. Infectious and gastrointestinal complications were the most common. Cardiopulmonary complications occurred in 2 of patients. ASA score (p = 0.049) and type of procedure (p<0.05) were significantly associated with the development of complications. When compared with patients <75 years, complication rates showed a trend but were not significantly higher in the elderly patients (p>0.05 for all surgery subgroups). (Figure 1)
CONCLUSIONS: Elderly patients undergoing robotic surgery did not have a significantly higher rate of early postoperative complications. Complications were more common with high ASA score and robotic cystectomy.
Back to Annual Meeting Program
|