|
|
 |
Back to Annual Meeting Program
Multicenter Phase III REDECT Trial with 124I-Girentuximab Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography (PET/CT) for the Presurgical Detection of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ccRCC)
John A. Libertino, MD1, Robert G. Uzzo, MD2, Paul Russo, MD3, David Chen, MD2, Steven Larson, MD3, Robert Bahnson, MD4, Paul Bevan, PhD5, Norman Neville, MD5, Silke Treutner, not applicable5, Roman Bartz, PhD5, Chaitanya R. Divgi, MD6.
1Lahey Clinic, Burlington, MA, USA, 2Fox Chase Cancer Center, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 3Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, USA, 4Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 5Wilex AG, Munich, Germany, 6Kreitchman PE Center, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, USA.
Multicenter Phase III REDECT Trial with 124I-Girentuximab Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography (PET/CT) for the Presurgical Detection of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ccRCC)
Background: The ability to distinguish preoperatively between ccRCC and other renal masses may help patients avoid surgical overtreatment.
The antibody girentuximab (cG250) binds to carbonic anhydrase-IX (CAIX), which is expressed in >95% of ccRCC. Results from a recent phase III study to determine the specificity/sensitivity of presurgical PET/CT using 124I-girentuximab for detecting ccRCC vs multiphasic diagnostic CT is presented.
Methods: 14 study sites included patients with a renal mass and no metastases other than from primary tumor. Histopathology and imaging studies were assessed via a blinded, centralized process.
Results: 226 patients; 63% men; mean age 56 years (range, 24-87 y). Surgery was conducted in 202 patients; 196 had evaluable PET/CT and diagnostic CT imaging and provided renal tumor tissue for histopathologic diagnosis. 146 patients had ccRCC (72.3%); 143 had evaluable images; 56 had non-ccRCC (27.7%); 53 had evaluable images. Diagnostic efficacy data is outlined (Table). Only 1 serious adverse event possibly related to study agent was reported.
Conclusions: PET/CT with 124I-girentuximab reliably distinguished ccRCC from less-aggressive subtypes and improved presurgical histologic diagnosis vs CT. Detection of aggressive ccRCC using 124I-girentuximab-PET/CT might reduce unnecessary surgeries and appropriately guide patient management. 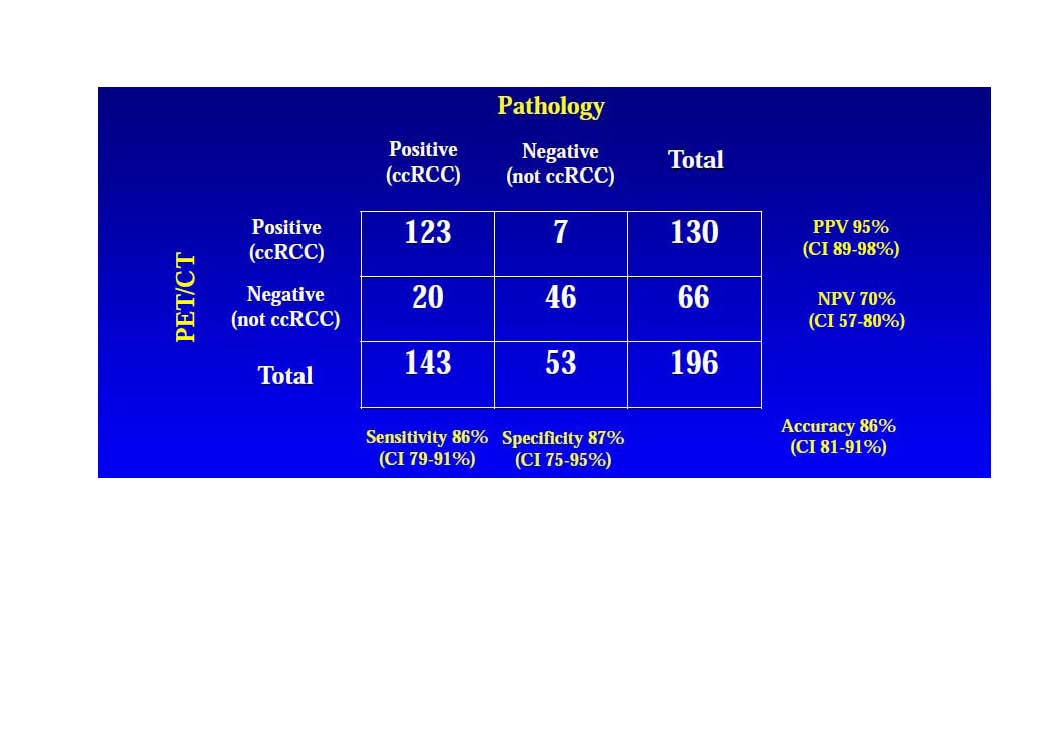
Back to Annual Meeting Program
|